

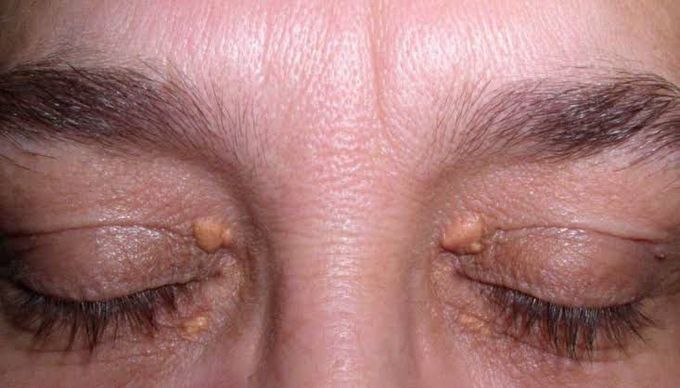
Xanthelasma palpebrarum
The word "xanthelasma" is made up of "xanth-" from the Greek roots "xanthos" (yellow) and "elasma" (plate); a yellow plate, so called because these are yellow plaques. Tiny (1-2 mm) yellowish plaques that are slightly raised on the skin surface of the upper or lower eyelids. Xanthelasma is caused by tiny deposits of fat in the skin and is often associated with abnormal blood fat levels (hyperlipidemia). Xanthelasma is a harmless growth of tissue. Xanthelasma typically appears in or near the eyelids. Under the microscope, Xanthelasma can be seen to be composed of lipid-laden foam cells. These cells, termed histiocytes, contain lipid material in their cytoplasm (the nonnuclear zone of the cell).
Treatment is Surgical excision Cryotherapy Laser Tropical chemical peeling Monitor lipid profile.


