

Hiba Iqbalover 4 years ago
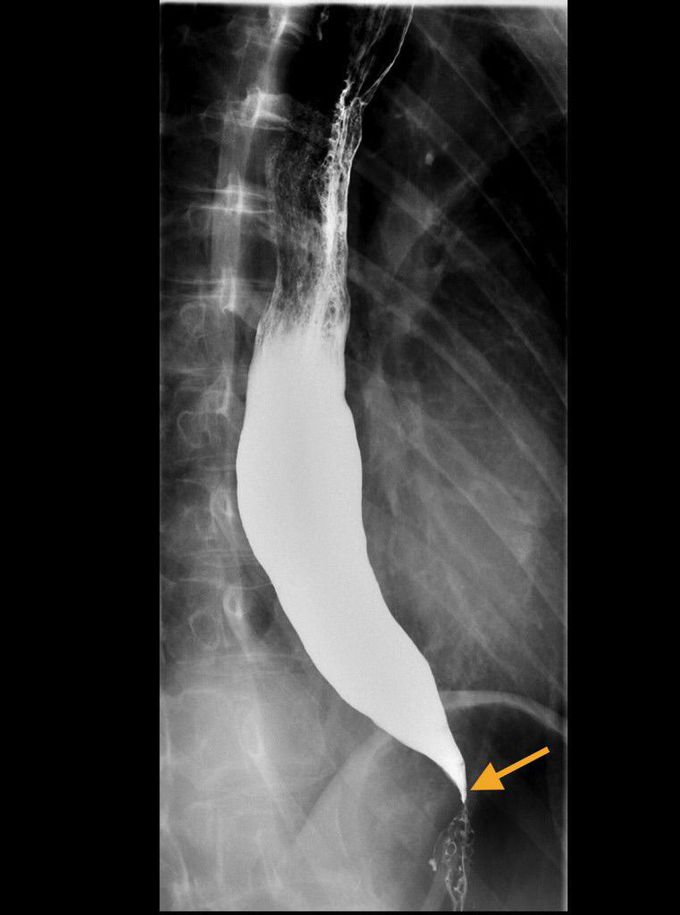
Achalasia
Achalasia is the inability of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) to relax due to loss of myenteric plexus within lower esophagus. What is the most likely diagnosis? Look for: - Young patient, under 50 - Progressive dysphagia - No association with alcohol/tobacco Diagnostic test: - Barium esophagram will show a 'Bird's Beak' as esophagus comes down to a point. - Manometery is most accurate test. - CXR shows widening of esophagus but not a specific test. - Endoscopy is useful to exclude malignancy. Treatment: - Pneumatic dilation, effective in 80-85% of patients. - Surgical sectioning or Myotomy is most effective. - Botulinum toxin injection; but effects wear off in 3-6 months, require reinjection.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!



