

Ramsha Zaheerover 4 years ago
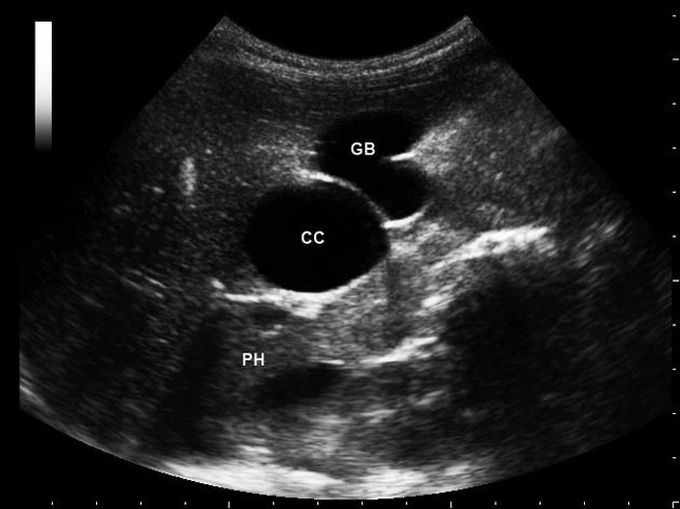
Choledochal Cysts
Choledochal cysts refer to cystic dilatations of the biliary tree involving either the intra-hepatic or extra-hepatic ducts, or both. They are more common in women than men. Clinical features include epigastric pain, fever, jaundice, and RUQ mass. Cholangiocarcinoma is one of the most feared complications of choledochal cysts. Other complications include recurrent cholangitis/pancreatitis, liver abscess, biliary obstruction, portal hypertension, and cirrhosis. Ultrasound is the best non-invasive test for the diagnosis. However, a definitive diagnosis is made by ERCP. Treatment includes complete resection of the cyst with a biliary-enteric anastomosis to restore continuity of the biliary system with bowels.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!

