

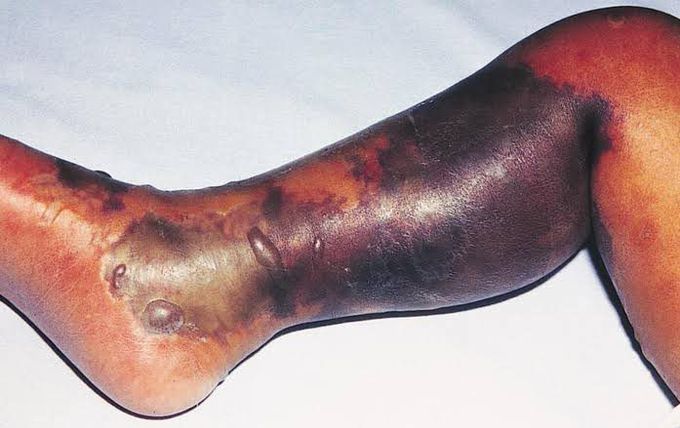
Necrotizing Fasciitis
Necrotizing fasciitis is a bacterial infection of fascia along with necrosis of subcutaneous tissue. It is an aggressive infection that commonly involves Group A beta-hemolytic streptococci, Staphylococci, Anaerobes and Gram negative rods. These organisms are transmitted through surgical wounds, injuries, cuts, burns, bites and abrasions. Signs and symptoms of necrotising fasciitis includes The condition presents with fever, pain, redness and swelling of the area that progresses to cellulitis or abscess and ultimately leads to bullae formation, bleeding and necrosis of the involved tissue. Risk factors includes immune suppression, diabetes, obesity, alcoholism, intravenous drug use and malignancy. Picture credit: https://www.orthobullets.com/trauma/1007/necrotizing-fasciitis
This condition can be life threatening so immediate admission is required. 1. Immediately start antibiotic treatment intravenously starting with the broad spectrum antibiotics and then shifting to culture specific antibiotics. 2. Surgical debridement of the involved area to remove the damaged or necrosis tissue 3. Daily antibiotic dressing (silver sulfadiazine is commonly used) 4. Amputation may be required in severe cases 5. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy 6. IV fluid support to prevent hypotension along with nutritional support and intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIG)

