

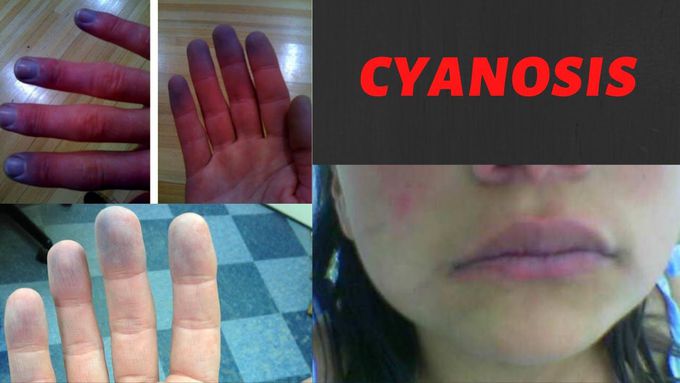
Cyanosis
Cyanosis is defined as a bluish discoloration, especially of the skin and mucous membranes, due to excessive concentration of deoxyhemoglobin in the blood caused by deoxygenation. Cyanosis is divided into two main types: central (around the core, lips, and tongue) and peripheral (only the extremities or fingers). Cyanosis occurs when oxygen-depleted (deoxygenated) blood, which is bluish rather than red, circulates through the skin. Cyanosis can be caused by many types of severe lung or heart disease that cause levels of oxygen in the blood to be low. Doctors diagnose peripheral cyanosis through a combination of physical tests, imaging scans, such as X-rays, and blood tests. These tests can identify the presence of other conditions that affect the heart or lungs or that alter the body's normal oxygen levels. The treatment involves identifying and correcting the underlying cause in order to restore the oxygenated blood flow to the affected parts of the body. And using drugs that help in vessel relaxation like: antidepressants, antihypertensive drugs, erectile dysfunction drugs. Avoiding certain medications that constrict blood vessels as a side effect. These include types of: beta-blockers, migraine medications, birth control pills, pseudoephedrine-based cold and allergy medicines. Serious medical situations, such as heart or pulmonary related conditions, should be treated in a hospital as an emergency. Conditions, such as Raynaud’s phenomenon, may require longer term lifestyle changes. These include avoiding caffeine and nicotine, both of which can cause your blood vessels to constrict

