

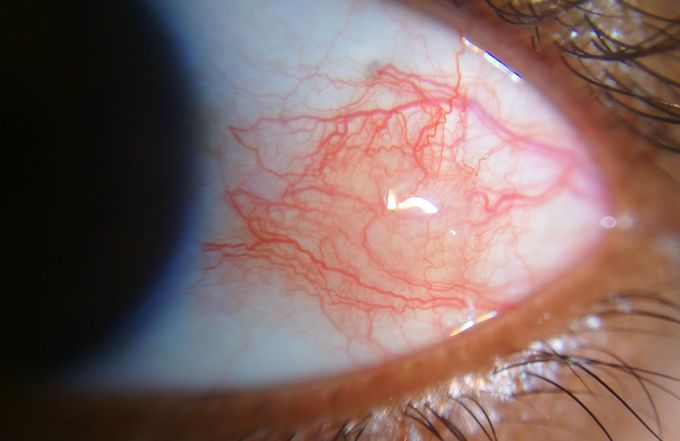
EPISCLERITIS
It is inflammation of the episcleral tissue which is between the conjunctiva and the sclera. It is a common, self limiting disease and its etiology is unknown. There are no specific risk factors for this disease but a small number of patients have an associated systemic disease like systemic lupus erythematosus, reactive arthritis or rheumatoid arthritis. The classic presentation is that of a red eye which may or may not be associated with pain. Sometimes the redness takes on a nodular appearance and in that case, it is termed as "nodular episcleritis". The nodular form of episcleritis is self limiting too but it takes slightly longer to resolve compared to simple episcleritis. The diagnosis is made clinically and as stated above, no specific treatment is required apart from supportive measures like cool compresses. However, in recurrent cases oral or topical NSAIDs can be prescribed for pain relief.
Living with Lupus is often a battle not just against the illness itself, but also against the emotional weight of uncertainty, fatigue, and the toll of long-term medications. For one courageous woman, that battle began in 2013. Diagnosed after Lupus had already affected her joints and internal organs, she was quickly placed on medication that initially helped. But as time went on, her health declined again this time with more frequent flare-ups and increasingly difficult side effects. Like many others with chronic illness, she faced the crushing weight of hopelessness. Each day became harder than the last, and conventional treatments no longer offered the comfort they once did. But in March 2020, at her lowest point, she made a decision that changed everything.Out of desperation and with a healthy dose of skepticism she turned to NaturePath Herbal Clinic, hoping their natural Lupus treatment might offer at least some relief. What happened next went far beyond her expectations.After completing a six-month herbal program, her flare-ups stopped entirely. Her energy returned. The chronic pain that had defined her daily life began to fade. For the first time in years, she felt like herself again. Not just alive but truly living.Her story is not just one of healing; it’s one of resilience, open-mindedness, and the courage to try something new when all else fails. By sharing her journey, she hopes to offer something priceless to others living with Lupus: hope.This treatment has been a true breakthrough for her. If you’re searching for a safe, natural, and effective alternative, I genuinely recommend giving this a chance.”www.naturepathherbalclinic.com or email them at info@naturepathherbalclinic.com


