

Mishal Shan10 months ago
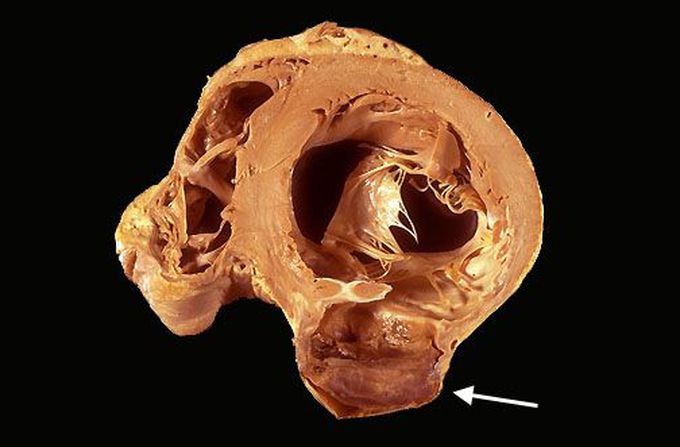
Ventricular Aneurysm post-MI
Aneurysm is a localized dilatation in a vascular/ heart wall. Myocardial infarction leads to weakening of the muscular wall of the heart which can then bulge out under increased intraventricular pressure. This sac does not contain enough cardiac muscle to contract efficiently which leads to two problems: The portion of the heart is unable to pump which decreases stroke volume and cardiac output. Secondly, this sac acts as a site of blood stasis. Stagnant blood then clots and is prone to embolize to any other artery. This can cause end organ ischemia, the presentation of which will depend on the artery involved. It may terminate in stroke or acute limb ischemia. Image via: https://webpath.med.utah.edu/TUTORIAL/MYOCARD/MI030.html
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!

