

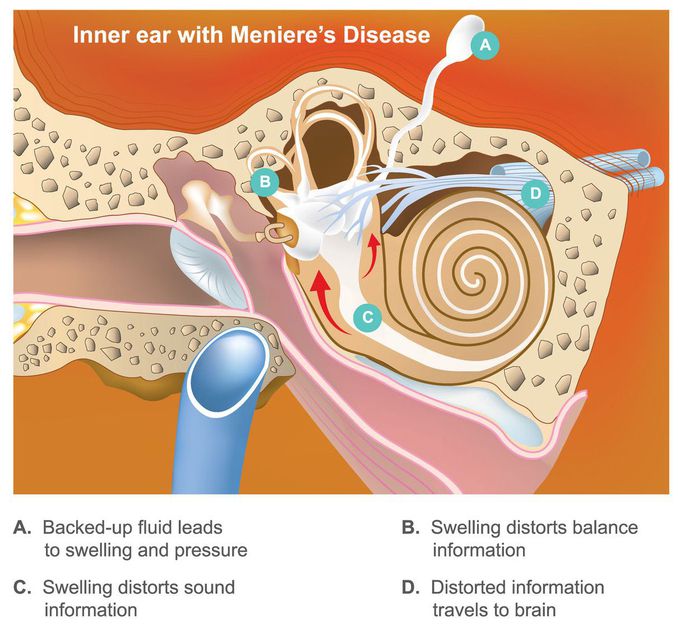
Meniere's disease
The disorder of inner ear characterised by increased endolymph. It is more common in women. Patient presents with recurrent episodes of severe vertigo, hearing loss, tinnitus and ear fullness, episodes often lasting minutes to hours. Nausea and vomiting are typical. Patient progressively lose low-frequency hearing over years and may become deaf on the affected side. Before diagnosis you must rule out cerebellopontine angle (CPA) tumors by doing MRI. Two episodes lasting more than 20 minutes with remission of symptoms between episodes, hearing loss documented at least once with audiometery and tinnitus or aural fullness are needed to make the diagnosis once other causes (eg, TIA, otosyphilis) have been ruled out. Meclizine or benzodiazepines are given in acut cases to control spinning sensation which are often very irritable to patient. Antiemetics given for nausea/vomiting. For chronic history, dietary changes should be made to limit salt intake to avoid fluid retention. For severe unilateral cases, intratympanic injection of gentamicin into middle ear (absorbed by inner ear) has been shown to reduce severity and frequency of vertigo attack.

