

Infective gastroenteritis (Acute diarrhoea)
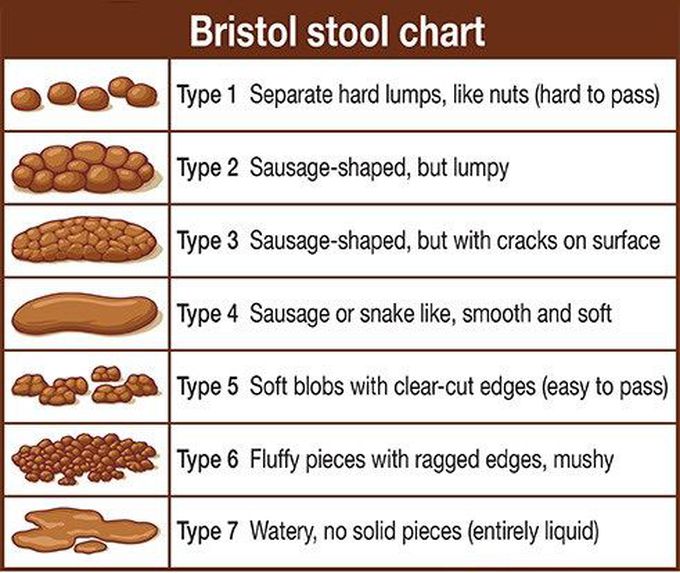
Acute diarrhoea and mild vomiting is predominant symptom in gastroenteritis. Diarrhoea is a symptom of infective and non infective causes along with stress either psychological or physical can also produce loose stools. The infection spreads majorly via feacal-oral route. Orgamisms like Staph. aureus, Vibrio cholera, Bacillus elute exotoxins that leads to vomiting and cause Secretory diarrhoea( watery diarrhoea without blood). Shigella spp., Compylobacter spp. and enterohaemorrhagic E. coli(EHEC), directly invades the mucosa of small bowel leads to ulceration and causes Bloody diarrhoea(with blood in stools). Salmonella typi and Salmonella paratyphi(enteric fever) particularly affects immune compromised and elderly. For clinical assessment history of frequency, presence of blood(steatorrhoea), abdominal pain, tenesmus and whether other people affected should be addressed. Early signs of hypotension, such as thirst, headache, altered skin turgor, dry mucous membranes shows signs of dehydration. The severity of diarrhoea can be assessed by reference to Bristol stool chart shown in picture above. Stool culture should be performed to look for toxins and species causing diarrhoea. Appropriate management of acute diarrhoea is initial isolation to minimise person to person spread followed by fluid replacement and antimicrobial agents. Antidiarrhoeal or antimotility agents are not usually recommended in acute infective diarrhoea.

