

Polyps in the Large Intestine
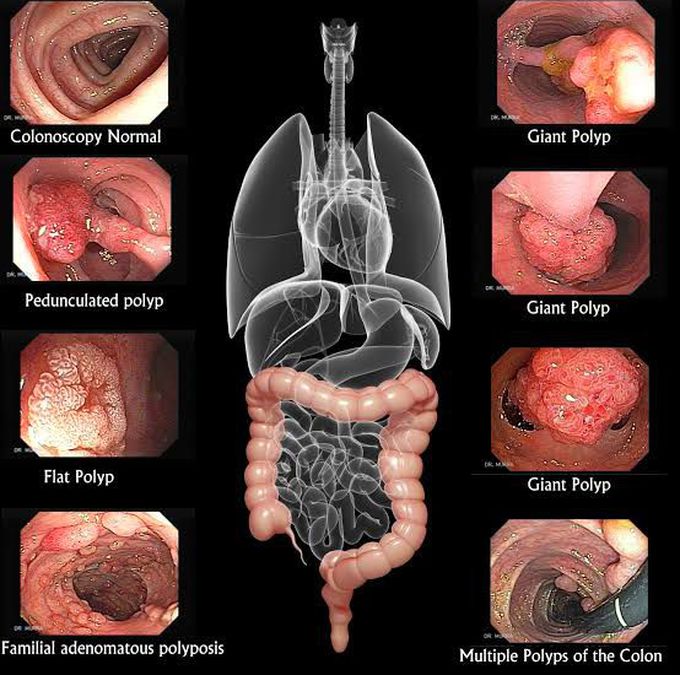
Polyps are mucosal outgrowths protruding into the organ's lumen. They are frequently encountered in the rectum and sigmoid colon. They can be of the following types: 1. Inflammatory pseudopolyps: They are formed as a result of edema of the mucosa and are usually associated with colitis. 2. Juvenile polyps: These are bright red and pedunculated, also referred to as cherry tumours. When solitary, they pose no risk of malignancy but if multiple, they might carry an increased risk of neoplastic changes. A characteristic histological feature is the presence of mucous filled spaces within the polyp. 3. Hyperplastic polyps: These polyps are small, sessile and often multiple. They do not usually carry a malignant potential. 4. Adenomatous polyps: These may be of the tubular, villous or tubulovillous variety. They have an increased risk of malignancy, especially if their size exceeds 1cm. FAP or familial adenomatous polyposis is a hereditary disorder characterized by numerous adenomatous polyps in the colon. This condition necessitates prophylactic colectomy to prevent the occurence of colonic adenocarcinoma. Ideally all polyps should be biopsied or removed to exclude cancer! Image via: http://www.gastrointestinalatlas.com/murrasaca/english/polyps.html Source: Bailey and Love's Short Practice of Surgery

