

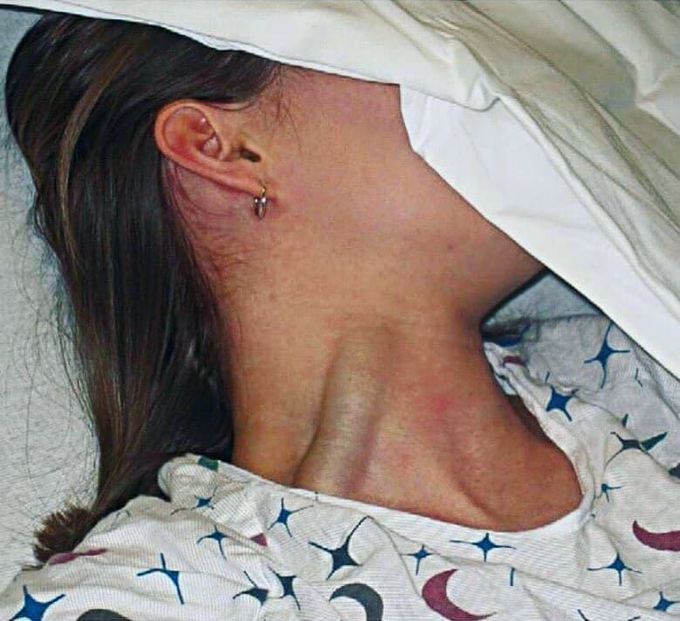
Jugular vein distention, which is quite massive, in a woman with cardiac tamponade! Jugular vein distention occurs when the pressure inside the vena cava increases and appears as a bulge running down the right side of a person's neck. A person has jugular veins on both sides of their neck. They act as passageways for blood to move from a person's head to the superior vena cava, which is the largest vein in the upper body. The superior vena cava then transports the blood to the heart and lungs. Jugular vein distention or JVD is when the increased pressure of the superior vena cava causes the jugular vein to bulge, making it most visible on the right side of a person's neck. The blood flow from the head to the heart is measured by central venous pressure or CVP. The appearance of the vein is similar to a rope or raised tube below the surface of the skin, and its height can be measured to indicate the CVP. There are several reasons why JVD may occur, and these include right-sided heart failure, tricuspid valve stenosis, pulmonary hypertension, constrictive pericarditis, superior vena cava obstruction, and cardiac tamponade. In cardiac tamponade, we look for 3 things, one of them you can see in the picture. These 3 things are called Beck's triad which is a collection of three medical signs associated with acute cardiac tamponade, an emergency condition wherein fluid accumulates around the heart and impairs its ability to pump blood. The signs are low arterial blood pressure, distended neck veins, and distant, muffled heart sounds. Credit to: @medicaltalks
Hemodynamic stimuli&nonhemodynamic stimuliEffects of sugar on teeth

