

Medicalpediaover 5 years ago
#NSFWSensitive content 18+
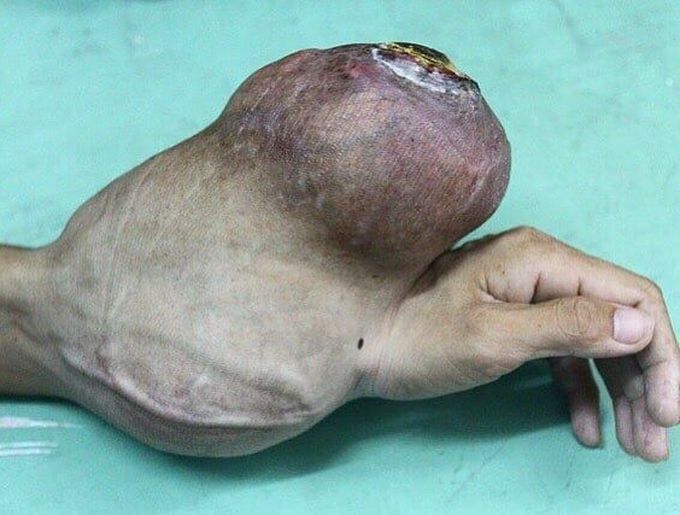
This material contains content which some users might find distrubingUntreated giant cell tumor of the lower arm!
Giant cell tumor of the bone is a rare, aggressive non-cancerous tumor. It generally happens in adults between ages 20 and 40 when skeletal bone growth is complete. It usually develops near a joint at the end of the bone. The location of a giant cell tumor is often in the knee, but can also involve the bones of the arms and the legs. While the exact cause of giant cell tumors remains unknown. Symptoms may include joint pain, swelling, and limited movement. The goal for treatment of a giant cell tumor is to remove the tumor and prevent damage to the affected bone. Tumors that can’t be removed surgically can often be controlled and sometimes destroyed with radiation therapy. Credit: HopkinsMedicine.Org
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!
Related posts
49.A 17-year-old boy took a tablet X for a headache. Drug X is a weak acid with a pka of 6.8. What percentage of the drug was most likely water soluble in the patient's plasma? Select one:
a. 80%
b. 65%
c. 99%
d. 1%
e. 52%DERMOGRAPHISM ?WelcomeMental and physical health are interconnected. We, as a society, need to work on emphasizing the importance of the two. This would prevent people developing physical and mental diseases at earlier and earlier ages.Marfan syndrome
Hemodynamic stimuli&nonhemodynamic stimuliEffects of sugar on teeth
Hemodynamic stimuli&nonhemodynamic stimuliEffects of sugar on teeth

