
Case 2
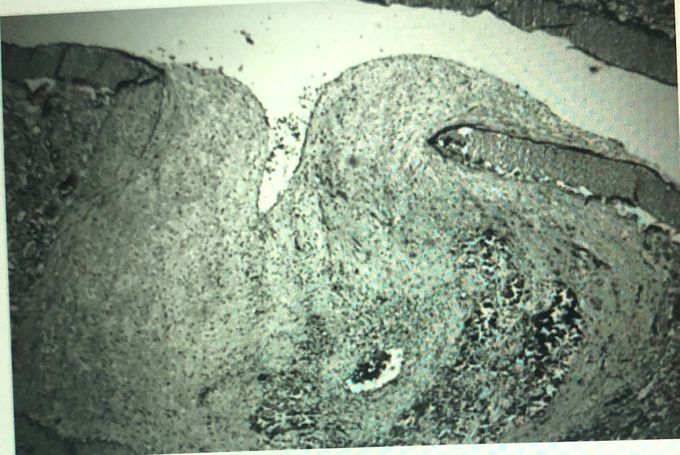
A 28-year-old African-American man presents to the physician with fever, weight loss, and abdominal pain. His blood pressure is 168/92mm Hg, his pulse is 83/min, and his respiratory rate is 18/min. On physical examination, there is palpable purpura on his lower extremities; a fundoscopic examination reveals fluffy, white spots on his retina. His past medical history is significant for a previous hepatitis B infection. An arterial biopsy is shown in the image. Which of the following is the most prominent morphologic feature of the affected arteries in this patient’s disease process? *  A- Caseating necrosis B- Eosinophilic infiltrate C- Fibrinoid necrosis D- Granulomatous infl ammation E- Langhans’ giant cells F- Onion skinning
I was diagnosed as a Hepatitis B carrier in 2015, with early signs of liver fibrosis. At first, antiviral medications helped control the virus but over time, resistance developed, and the effectiveness faded. I began to lose hope. In 2021, I discovered NaturePath Herbal Clinic despite my skepticism, I decided to give their herbal treatment a try.To my surprise, after just six months, my blood tests came back negative for the virus.It was nothing short of life-changing.I never expected such incredible results from a natural treatment. But it not only cleared the virus it restored my hope, my health, and my peace of mind.If you or someone you know is battling Hepatitis B, I truly encourage you to explore the natural healing path offered by NaturePath Herbal Clinic. It gave me a second chance and it might do the same for you.www.naturepathherbalclinic.com info@naturepathherbalclinic.com


