

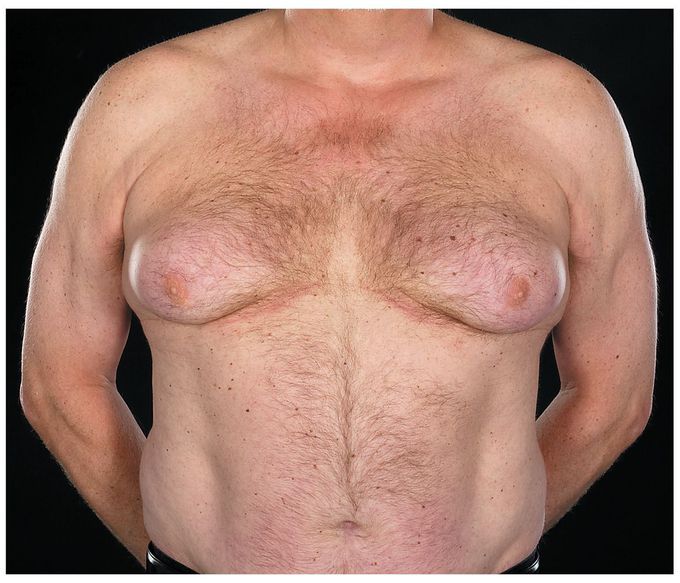
Gynecomastia Induced by Prostate-Cancer Treatment
A 60-year-old man presented to the breast clinic with gynecomastia. A high-grade, advanced prostate cancer (T3N1M0; Gleason score, 9 [grade 4 plus grade 5]) had been diagnosed 4 years earlier, and the patient was treated with radiotherapy and adjuvant hormonal therapy. Hormonal treatment consisted of an androgen-receptor inhibitor (bicalutamide at a dose of 150 mg daily) for 2.5 years. Six months after the initiation of treatment, progressive enlargement of the breasts developed, with pain bilaterally. After therapy was discontinued, the pain resolved; however, the size of the breasts remained static and caused the patient considerable social embarrassment. Examination of the breasts did not reveal any suspicious abnormality. Surgical correction was performed. Gynecomastia occurs in up to 80% of patients who receive nonsteroidal antiandrogens (e.g., bicalutamide, flutamide, or nilutamide), usually within the first 6 to 9 months after the initiation of treatment.

