

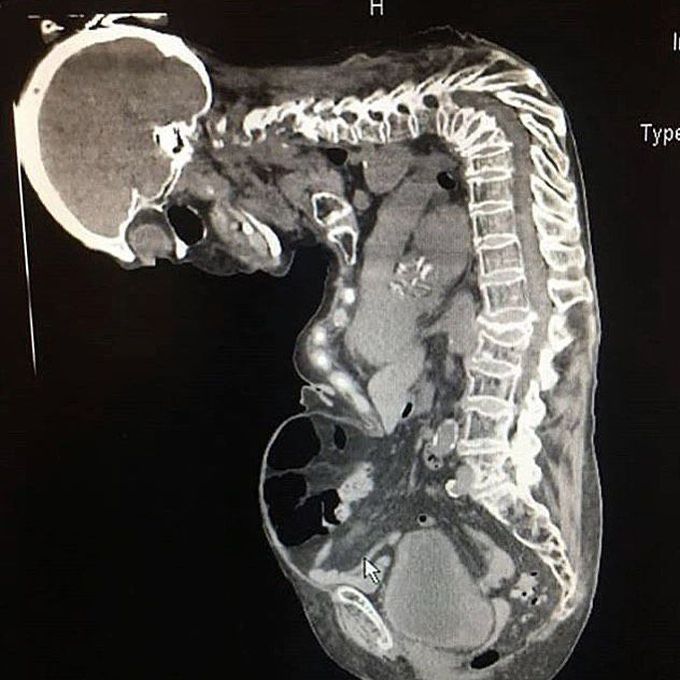
Extreme case of gibbus deformity!! ☠️
Gibbus deformity is a short-segment structural thoracolumbar kyphosis resulting in sharp angulation. The anterior collapse of one or more vertebral bodies resulting in kyphosis of a very sharp angle, as seen here. It is typically found in the upper lumbar and lower thoracic vertebrae, where one or more adjacent vertebrae become wedged. It often develops in young children as a result of spinal tuberculosis and is the result of collapse of vertebral bodies due to spinal infection and osteomyelitis. This can in turn lead to spinal cord compression causing paraplegia, as well as myelopathy, if untreated. In addition to tuberculosis, other possible causes of gibbus deformity include pathological diseases, hereditary and congenital conditions, and physical trauma to the spine that results in injury. Gibbus deformity may result from the sail vertebrae associated with cretinism (the childhood form of hypothyroidism), mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS), and certain congenital syndromes, including achondroplasia. Because most children with MPS I (Hurler Syndrome) also exhibit symptoms of a gibbus deformity, the latter can possibly be used to identify the former. Gibbus deformity is included in a subset of structural kyphosis that is distinguished by a higher-degree angle in the spinal curve that is specific to these forms of kyphosis. Other conditions within this subset include Pott’s disease and Scheuermann kyphosis, but gibbus deformity is marked by an especially sharp angle. Viewed from behind, the resulting hunchback is more easily seen when bending forward. A kyphosis of >70° can be an indication of the need for surgery and these surgeries can be necessary for children as young as two years old, with a reported average of 8 years of age. Patients complain of mid-back pain and stiffness. Treatment for Gibbus deformity, caused by infectious sources, requires both antibiotics to treat osteomyelitis as well as surgical correction which usually involve corpectomy, interbody cage placement, and posterior instrumentation and fusion.
Hemodynamic stimuli&nonhemodynamic stimuliEffects of sugar on teeth

