

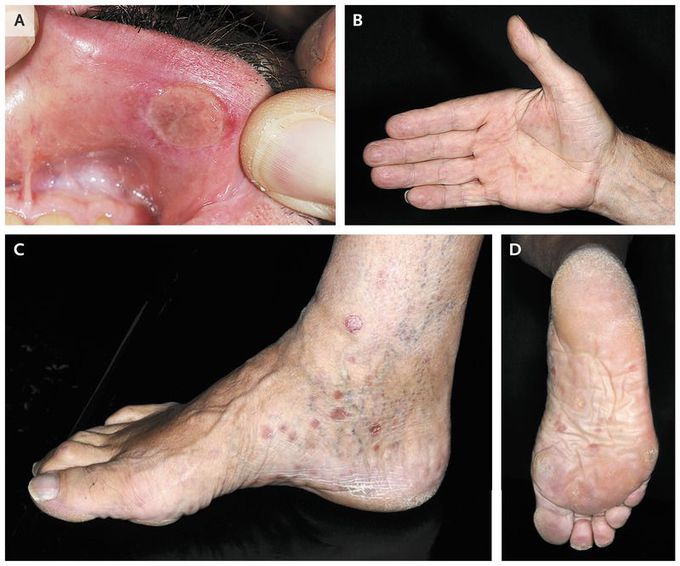
Primary and Secondary Syphilis
A previously healthy 68-year-old man presented with a solid erosive sore on the inner aspect of his upper lip (Panel A). The painless lesion had been present for approximately 6 weeks. On examination, the patient had sharply demarcated erythematous, scaly plaques on his hands and feet, including the palms and soles (Panels B, C, and D). The patient reported that the lesions were waxing and waning and had been present for more than 1 year. There were no other symptoms. Laboratory investigations revealed a positive Treponema pallidum particle agglutination assay (titer, 1:2560; normal value, <1:80) and a positive Venereal Disease Research Laboratory test (titer, 1:8; normal value, <1:2). Serologic tests for human immunodeficiency virus and hepatitis were negative. Immunoblot analyses were positive for syphilis-specific IgM and IgG. Histopathological analyses of biopsy specimens obtained from the lip lesion and a representative lesion from the foot showed ulceration of the lip lesion and psoriasiform hyperplasia of the foot lesion; both specimens were associated with abundant CD79a-positive plasma cells and masses of T. pallidum bacteria.Concomitant primary and secondary syphilis was diagnosed. Intramuscular injections of penicillin G benzathine (three injections in 4-week intervals at a dose of 2.4×106 IU) led to complete resolution of the lesions within 2 months and to substantially decreased titers on laboratory tests. The concomitant presence of primary and secondary syphilis in the same patient is unusual; however, it is possible to acquire a superimposed second infection.
I was diagnosed as a Hepatitis B carrier in 2015, with early signs of liver fibrosis. At first, antiviral medications helped control the virus but over time, resistance developed, and the effectiveness faded. I began to lose hope. In 2021, I discovered NaturePath Herbal Clinic despite my skepticism, I decided to give their herbal treatment a try.To my surprise, after just six months, my blood tests came back negative for the virus.It was nothing short of life-changing.I never expected such incredible results from a natural treatment. But it not only cleared the virus it restored my hope, my health, and my peace of mind.If you or someone you know is battling Hepatitis B, I truly encourage you to explore the natural healing path offered by NaturePath Herbal Clinic. It gave me a second chance and it might do the same for you.www.naturepathherbalclinic.com info@naturepathherbalclinic.com


