

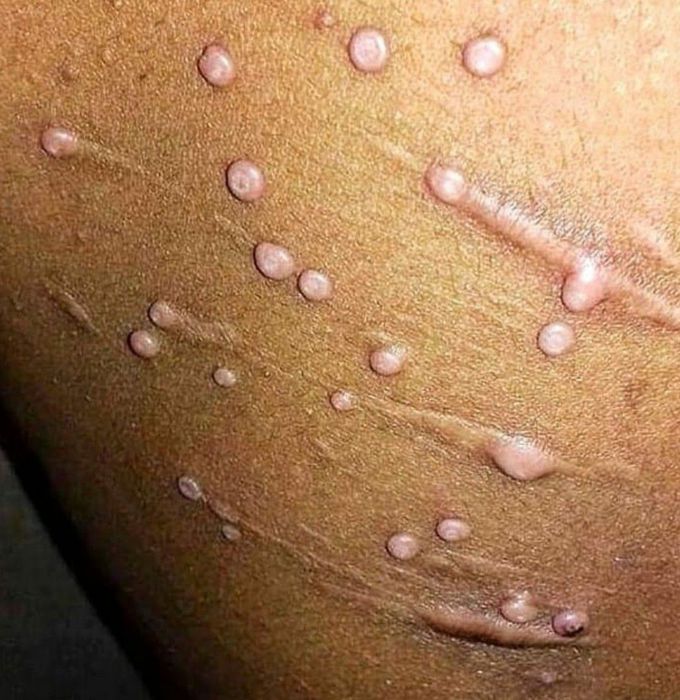
Molluscum contagiosum virus infection
causes the human disease molluscum contagiosum, which affects about 200,000 people a year or about 1% of all diagnosed skin diseases. The disease is diagnosed by a medical professional based on the size and shape of skin lesions and can be confirmed with a biopsy and cannot be routinely cultured molluscum contagiosum virus is the only species in the genus Molluscipoxvirus.Molluscum contagiosum virus is a member of the Poxviridae subfamily and Chordopoxvirinaesubfamily. Other commonly known viruses that reside in the Chordopoxvirinae subfamily are Variola virus (cause of smallpox) and Monkeypox virus.The poxvirus family is the only one that contains both non-enveloped and enveloped particles, which are termed mature virions and extracellular virions, respectively. The structure of the virions is consistent with that of others in the poxvirus family: they are composed of a nucleocapsid, core envelope, lateral body, and an extracellular envelope. Like other poxviruses, MCV is a DNA virus that replicates in the cytoplasminstead of the nucleus. Because of this, the virus must bring all necessary enzymes for replication with it or encode the enzymes in its genome.

