

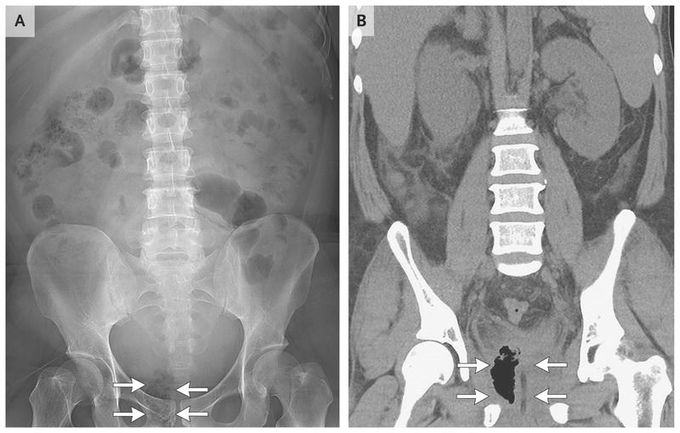
Emphysematous Prostatitis
A 42-year-old man with diabetes presented to the emergency department with severe dysuria and incontinence, which he had had for several days. Laboratory studies were notable for pyuria on urinalysis, leukocytosis (a white-cell count of 10,820 per cubic millimeter), elevated C-reactive protein levels (134.1 mg per liter), hyperglycemia (glucose level, 900 mg per deciliter [50 mmol per liter]), and an elevated level of glycated hemoglobin (11.4%). Radiography of the kidney, ureter, and bladder showed an atypical focus of gas accumulation behind the right pubic ramus (Panel A, arrows). Subsequent computed tomography (CT) of the abdomen revealed emphysematous prostatitis of the right prostate lobe (Panel B, arrows). A Foley catheter was placed, and CT-guided percutaneous drainage of the prostate was performed. Broad-spectrum antibiotics and intravenous fluid therapy were initiated, and strict blood sugar control was implemented with an insulin drip. Urine and blood cultures grew Klebsiella pneumoniae. The patient remained in the hospital for 1 month and was treated for infection, sepsis, poor control of blood sugar levels, and acute kidney injury. His condition gradually improved, and he was discharged home. Emphysematous prostatitis is a rare sequela of complicated urinary tract infection and is more commonly found in patients with immunosuppression, diabetes mellitus with poor glycemic control, liver cirrhosis, alcoholism, or recent urethral instrumentation. The most common pathogen in patients with diabetes, as in this case,

