
Zay Kabout 2 years ago
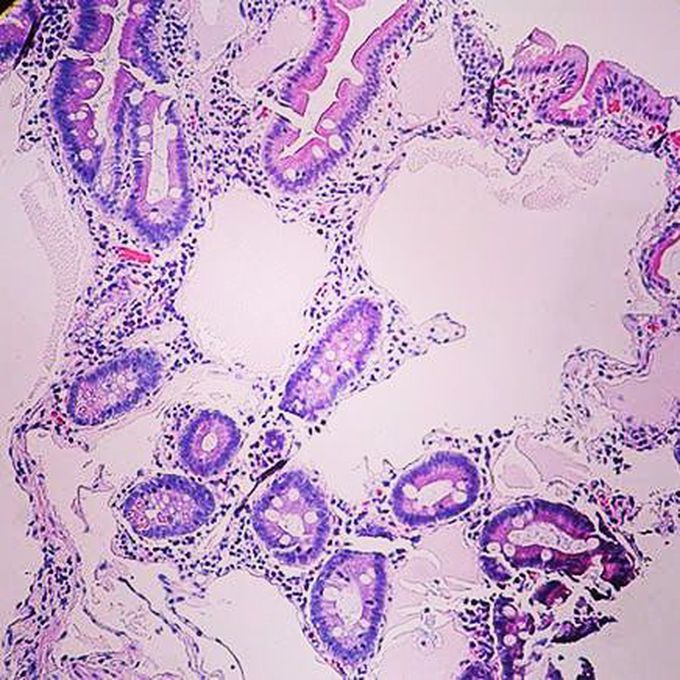
Pathology GI
Intestinal lymphangiectasia is a rare, benign disease characterized by hypoproteinemia, edema, and lymphocytopenia, resulting from focal or diffuse dilatation of intestinal mucosal, submucosal, and subserosal lymphatics and loss of lymph fluid into the gastrointestinal (GI) tract.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!

