

Human Papillomavirus–Associated Oropharyngeal Squamous-Cell Carcinoma
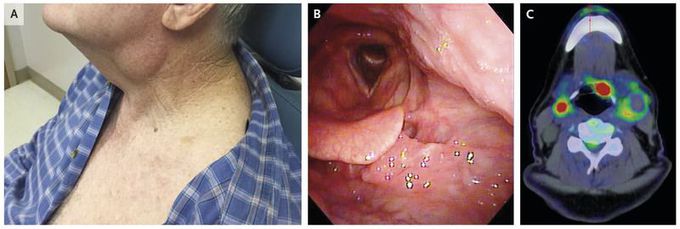
A 68-year-old man presented with a mass on the left side of his neck (Panel A). He had no history of tobacco use and drank one or two alcoholic drinks per week. A biopsy of the mass was performed, and histopathological examination revealed squamous-cell carcinoma that tested positive for human papillomavirus and overexpressed p16, a tumor-suppressor gene product. Flexible nasolaryngoscopy showed an exophytic mass on the left base of the tongue and epiglottic vallecula (Panel B). Positron-emission tomography showed uptake of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose in the vallecula and bilateral jugulodigastric lymphadenopathy (Panel C). Human papillomavirus–associated squamous-cell carcinoma occurs commonly in the oropharynx, even in patients who do not have the traditional risk factors for head and neck cancers, such as smoking and alcohol use. This patient was treated with radiation therapy with sensitizing chemotherapy and has recovered well, with no evidence of disease 7 months after treatment.

