

Dr. Aiswarya Vijayanover 6 years ago
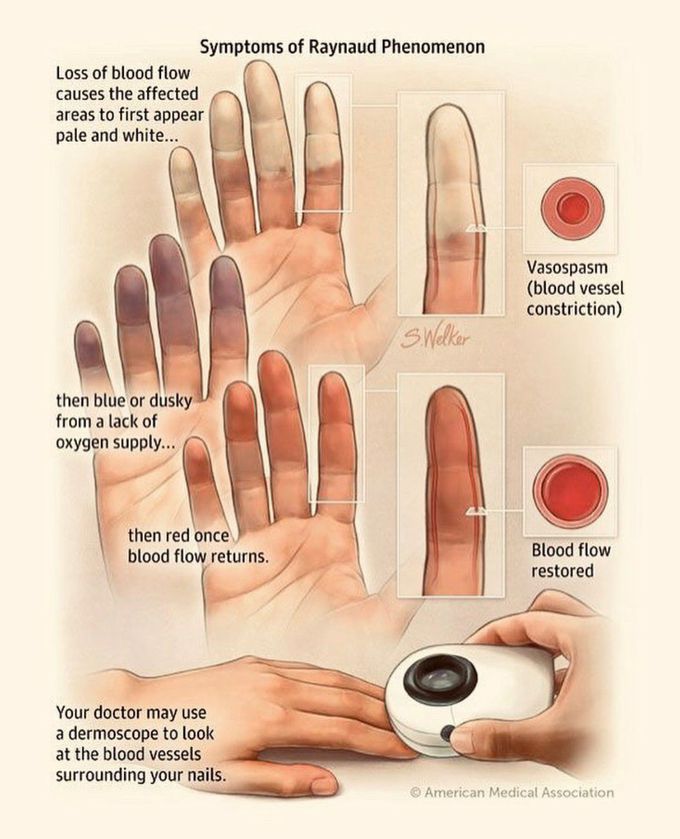
Raynaud's phenomenon
Raynaud's phenomenon is a type of vascular disease characterized by a pale to blue to red sequence of color changes of the digits, most commonly after exposure to cold. Raynaud's phenomenon occurs because of spasm of blood vessels. The cause of Raynaud's phenomenon is unknown, although abnormal nerve control of blood-vessel diameter and nerve sensitivity to cold are suspected of being involved. Symptoms of Raynaud's phenomenon depend on the severity, frequency, and duration of the blood-vessel spasm. There is no blood test for diagnosing Raynaud's phenomenon. Treatment of Raynaud's phenomenon involves protection of the digits, medications, and avoiding emotional stresses, smoking, cold temperature, and tools that vibrate the hands.


