
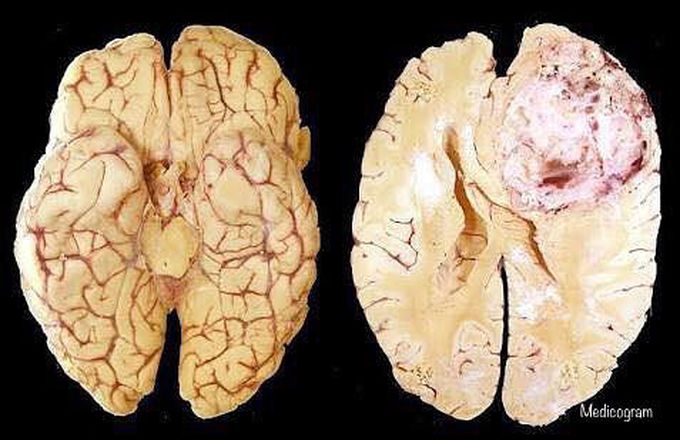
Glioblastoma: Glioblastomas (GBM) are tumors that arise from astrocytes—the star-shaped cells that make up the “glue-like,” or supportive tissue of the brain. These tumors are usually highly malignant (cancerous) because the cells reproduce quickly and they are supported by a large network of blood vessels. Location; Glioblastomas are generally found in the cerebral hemispheres of the brain, but can be found anywhere in the brain or spinal cord. Description Glioblastomas usually contain a mix of cell types. It is not unusual for these tumors to contain cystic mineral, calcium deposits, blood vessels, or a mixed grade of cells. Glioblastomas are usually highly malignant—a large number of tumor cells are reproducing at any given time, and they are nourished by an ample blood supply. Dead cells may also be seen, especially toward the center of the tumor. Because these tumors come from normal brain cells, it is easy for them to invade and live within normal brain tissue. However, glioblastoma rarely spreads elsewhere in the body. Symptoms; Because glioblastomas can grow rapidly, the most common symptoms are usually caused by increased pressure in the brain. These symptoms can include headache, nausea, vomiting, and drowsiness. Depending on the location of the tumor, patients can develop a variety of other symptoms such as weakness on one side of the body, memory and/or speech difficulties, and visual changes. Cause; Like many tumor types, the exact cause of glioblastoma is not known. Treatment; Glioblastoma can be difficult to treat because the tumors contain so many different types of cells. Some cells may respond well to certain therapies, while others may not be affected at all. This is why the treatment plan for glioblastoma may combine several approaches.

