

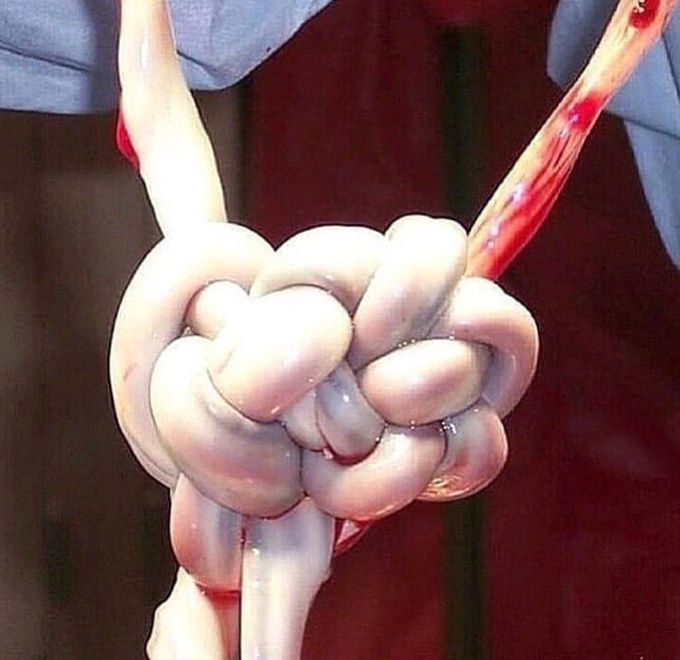
Umbilical cord knots
. There are two types of knots that can form in a baby’s umbilical cord: true knots and false knots. . False knots are actually slight variations in the cord’s anatomy, usually formed by swollen blood vessels or an excessive covering of Wharton’s jelly. . True knots forms when the umbilical cord loops or interweaves around itself. . True knots get more dangerous the closer a baby gets to birth, and in a worse-case scenario can cause asphyxia, leading to brain damage or death. Tight knots have a mortality rate of 10%. .
Is there a way to prevent this? What caused this? Excessive exercise that moves the baby around?
A true knot forms when the umbilical cord loops or interweaves around itself. They can form during pregnancy (when the baby's active and moves around in the amniotic fluid) and during birth. And a false knot is basically represents an exaggerated looping of the umbilical cord vessels, causing focal dilatation of the umbilical cord vessels. Cord knots occur in less than 2% of pregnancies. And I don't think it's really "preventable" because u can't control the baby's flipping in the womb.
Phineas Gage: A Case Study in Brain Injury and Personality Change
A 70-year-old man presents with difficulty walking, particularly when turning, and a sensation of his feet being "stuck" to the floor. His gait is characterized by hesitation and freezing when initiating steps. Which of the following is most likely to be observed in this patient? A. Spasticity B. Foot drop C.Freezing of gait D. Romberg signBest Probiotics For Womens 2025: Are They More Effective?Effects of sugar on teeth

