

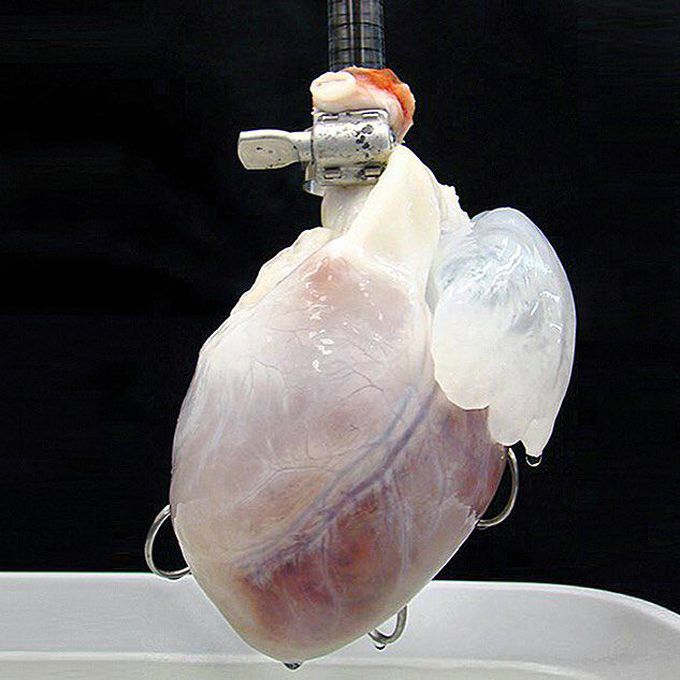
Decellularized heart with the vascular system still intact
In collaboration with @medspiration who made an informative video on his YouTube channel, I'd like to discuss with you all about the future of medicine, about the very close future of organ transplantations! Organ transplantation is still the ultimate treatment for end-stage organ failure. What if I told you that we can grow a heart (or any other organ) specifically for the patient in need? Without being concerned of rejection of the recipient, nor giving the patient tons of immunosuppressants which makes him prone to infections, bacterial and viral on top of the list. Decellularization is a tissue engineering technique designed to strip out all the cells from a donor organ, leaving nothing but the connective tissue that used to hold the cells in place. This scaffold of connective tissue can then be reseeded with a patient's own cells, with the goal of regenerating an organ that can be transplanted into the patient without fear of tissue rejection. The above photo shows a decellularized heart with the vascular system still intact, in which the cells have been stripped away, and the remaining scaffold has been infused with human stem cells to grow a new human heart, ready to go and save someone's life! Link in @medspiration 's page, feel free to subscribe to his YouTube channel if you like the video.

