

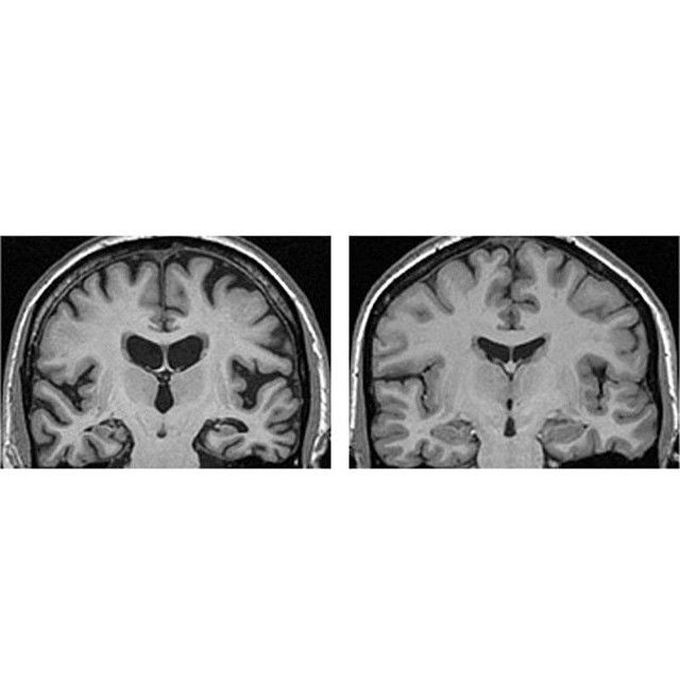
Comparison of a normal human brain MRI (right) and an MRI (left) taken from a patient with a well-known disease - Alzheimer's disease!
Loss of brain tissue (atrophy/degeneration) is seen well, shrinkage of the cerebral gyri of the temporal and parietal lobes, as well as the corpus callosum, fornix, caudate nucleus, and the hippocampus. All of which causes the dilation of the lateral and third ventricles (in the middle). Alzheimer's is a chronic neurodegenerative disease, and it's the most common cause of dementia, a general term for memory loss and other intellectual abilities. It's important to know that it's a progressive disease, where dementia symptoms gradually worsen over a number of years. In its early stages, memory loss is mild, but with late-stage Alzheimer's, individuals lose the ability to carry on a conversation and respond to their environment. The cause is poorly understood. It is believed that a build-up of beta-amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in the brain are associated with the disease. Other risk factors include a history of head injuries, depression or hypertension.No cure for Alzheimer's, but there are medications that slow the progression of the disease and manage the symptoms.
st experiences of my life. The memory loss, the confusion, and the fear of losing myself weighed on me every single day. I had tried so many treatments and medications, but nothing seemed to stop the disease from progressing.Out of both hope and desperation, I came across NaturePath Herbal Clinic. At first, I was skeptical, but something about their natural approach and the stories I read gave me the courage to try one more time.I began their herbal treatment program, and within a few weeks, I noticed small changes clearer thinking, better focus, and a calmer mind. Over the months, those improvements became more and more obvious. Today, I can truly say my life has changed. My memory has improved, and I feel more present and engaged than I have in years.This isn’t just a testimony it’s a heartfelt recommendation to anyone struggling with Alzheimer’s or other chronic conditions. Don’t give up hope. I’m so grateful I gave NaturePath Herbal Clinic a chance. Visit their website to learn more: www.naturepathherbalclinic.com info@naturepathherbalclinic.com



