
Epigastric pain and melena
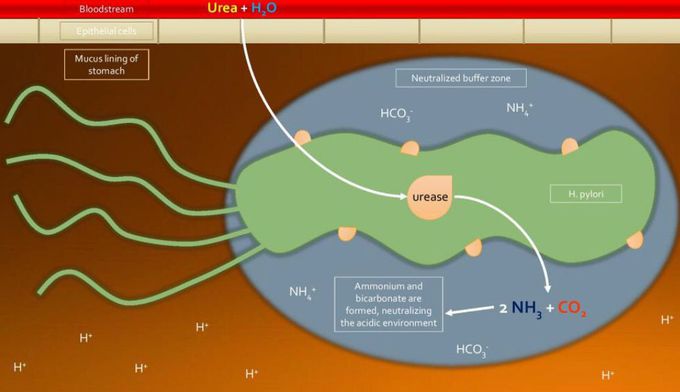
Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) is an ulceration in the stomach or duodenum that is caused by an imbalance between protective factors of the natural stomach lining and damaging mechanisms that predispose ulceration.Most duodenal ulcers (over 90%) occur in the first portion of the duodenum and gastric ulcers most commonly occur on the lesser gastric curvature near the incisura angularis. Duodenal ulcers are more common than gastric ulcer, occurring 4 times as frequent.Oftentimes the cause of PUD is multifold. The most common etiology of the damaging mechanisms is Helicobacter pylori infection, which is found in 70% of patients with PUD.The most common etiology that decreases natural protective factors of the gastric lining is medications such as NSAIDs. These reduce the body's natural production of prostaglandins.

