
Dr. Nuralievichover 8 years ago
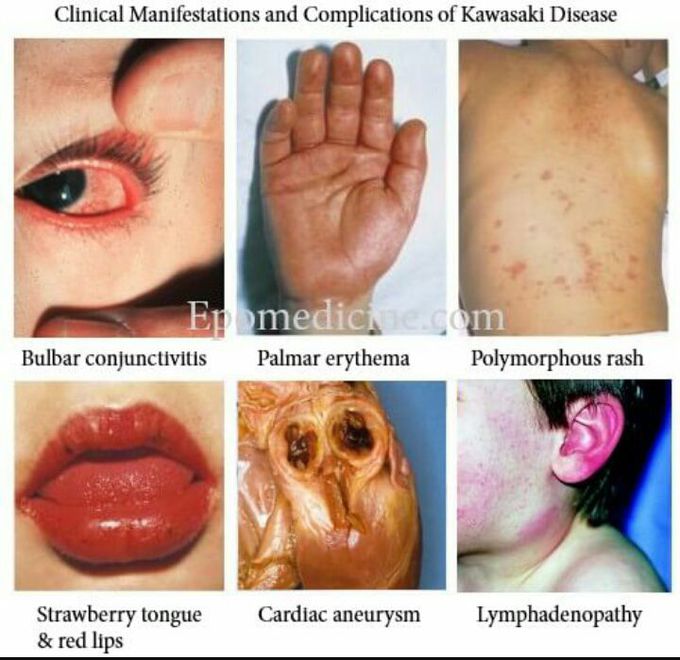
Kawasaki disease (KD) is an acute febrile vasculitic syndrome of early childhood that, although it has a good prognosis with treatment, can lead to death from coronary artery aneurysm (CAA) in a very small percentage of patients. Signs and symptoms Kawasaki disease produces prolonged fever (often abrupt in onset and preceded by several days of nonspecific symptoms) along with a constellation of clinical features that includes the following: Irritability Nonexudative bilateral conjunctivitis (90%) Anterior uveitis (70%) Perianal erythema (70%) Sterile pyuria Erythema and edema on the hands and feet; the latter impedes ambulation Strawberry tongue and lip fissures Hepatic, renal, and GI dysfunction Myocarditis and pericarditis Lymphadenopathy (75%); generally, a single, enlarged, nonsuppurative cervical node measuring approximately 1.5 cm.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!
Related posts
Diseases with Translocations
Pulpal and periapical diseasesDepressionEar tumors Ear tumors may be benign (noncancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Types of noncancerous ear tumors include keloids, sebaceous cysts, osteomas and exostoses (bone growths). Noncancerous ear tumors usually require surgical removal. Cancers that can affect your ears include melanoma, basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. Treatment for these conditions depends on several factors, including the type and stage of cancer, and whether or not it has spread to other parts of your body.Infectious vs Noninfectious diseases: Infectious diseases are caused by harmful organisms that get into your body from the outside, like viruses and bacteria. Noninfectious diseases aren’t caused by outside organisms, but by genetics, anatomical differences, getting older and the environment you live in. You can’t get noninfectious diseases from other people, by getting a bug bite or from your food. The flu, measles, HIV, strep throat, COVID-19 and salmonella are all examples of infectious diseases. Cancer, diabetes, congestive heart failure and Alzheimer’s disease are all examples of noninfectious diseases.Basal Ganglia DiseasesSymptoms of chronic liver disease
Autoimmune diseases
Pulpal and periapical diseasesDepressionEar tumors Ear tumors may be benign (noncancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Types of noncancerous ear tumors include keloids, sebaceous cysts, osteomas and exostoses (bone growths). Noncancerous ear tumors usually require surgical removal. Cancers that can affect your ears include melanoma, basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. Treatment for these conditions depends on several factors, including the type and stage of cancer, and whether or not it has spread to other parts of your body.Infectious vs Noninfectious diseases: Infectious diseases are caused by harmful organisms that get into your body from the outside, like viruses and bacteria. Noninfectious diseases aren’t caused by outside organisms, but by genetics, anatomical differences, getting older and the environment you live in. You can’t get noninfectious diseases from other people, by getting a bug bite or from your food. The flu, measles, HIV, strep throat, COVID-19 and salmonella are all examples of infectious diseases. Cancer, diabetes, congestive heart failure and Alzheimer’s disease are all examples of noninfectious diseases.Basal Ganglia DiseasesSymptoms of chronic liver disease
Autoimmune diseases

