

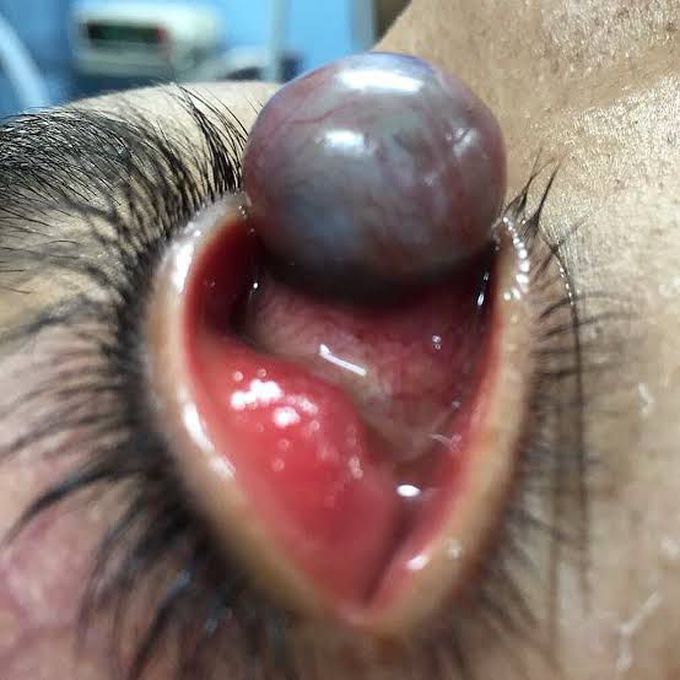
Anterior Staphyloma
Staphyloma refers to thinning (ectasia) of the uvea and scleral layers of the globe. It results in enlargement of the globe with a focal bulge, usually in the posterior wall. Anterior staphyloma can be the result of an inflammatory/infectious process or secondary to developmental defect, due to faulty differentiation of the anterior mesoderm. The congenital type is rare. Clinical Features: Patients usually present with enlarged, protruding, and opacified eye with loss of vision. Key Diagnostic Features: Imaging is needed to establish the presence or absence of a mass within the enlarged eye. In staphyloma, there is ectatic protruding cornea with focal out-pouching and enlargement of the anterior segment and without an intraocular mass. DDx: Bupothalmus (secondary to congenital glaucoma) Axial myopia Coloboma Rx: Penetrating keratoplasty Enucleation (in servere cases

