

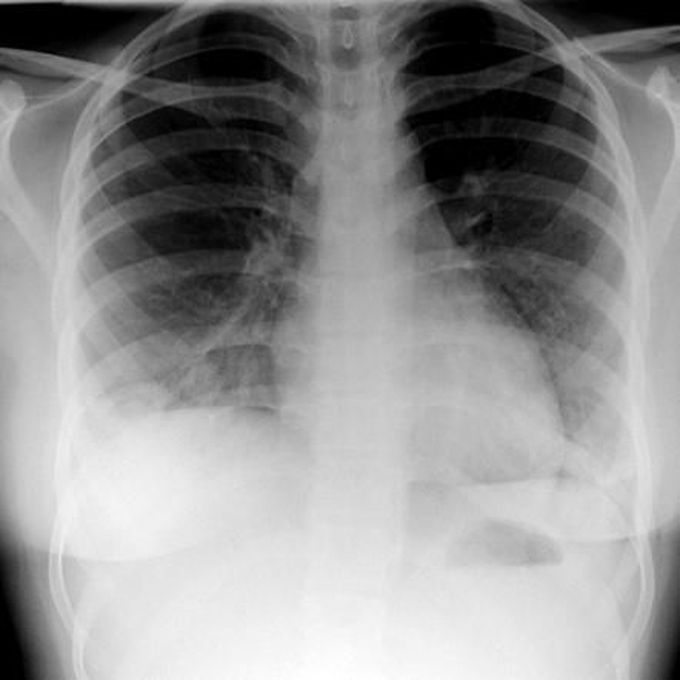
Wegener's granulomatosis
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (formerly called Wegener’s) is a rare disease of uncertain cause that can affect people of all ages. It is characterized by inflammation in various tissues, including blood vessels (vasculitis), but primarily parts of the respiratory tract and the kidneys. GPA primarily affects the upper respiratory tract (sinuses, nose, trachea [upper air tube]), lungs, and kidneys. Any other organ in the body can be affected as well. The symptoms of GPA and their severity vary among patients. General signs of the disease may include: Loss of appetiteWeight lossFeverFatigue Most patients first notice symptoms in the respiratory tract. Symptoms may include: Persistent runny nose (also called rhinorrhea) or the formation of nasal crusts and sores Nasal or facial painNose bleeds or unusual nasal discharge, caused by inflammation of the nose or sinusesCough that might include bloody phlegm caused by upper airway or lower airway (lung) inflammationChest discomfort with or without shortness of breathMiddle ear inflammation (also called otitis media), pain, or hearing lossVoice change, wheezing, or shortness of breath caused by inflammation of the trachea
Immunosupressive drugs like cyclophosphamide can be use for this.Intravenous immunoglobulin therapy (IVIG) has been shown to be helpful in treating relapses of granulomatosis with polyangiitis.
Pulmonary Wegener's granulomatosis can present with multifocal lung involvement or solitary lung lesions with no evidence of extrapulmonary disease


