

Trauma
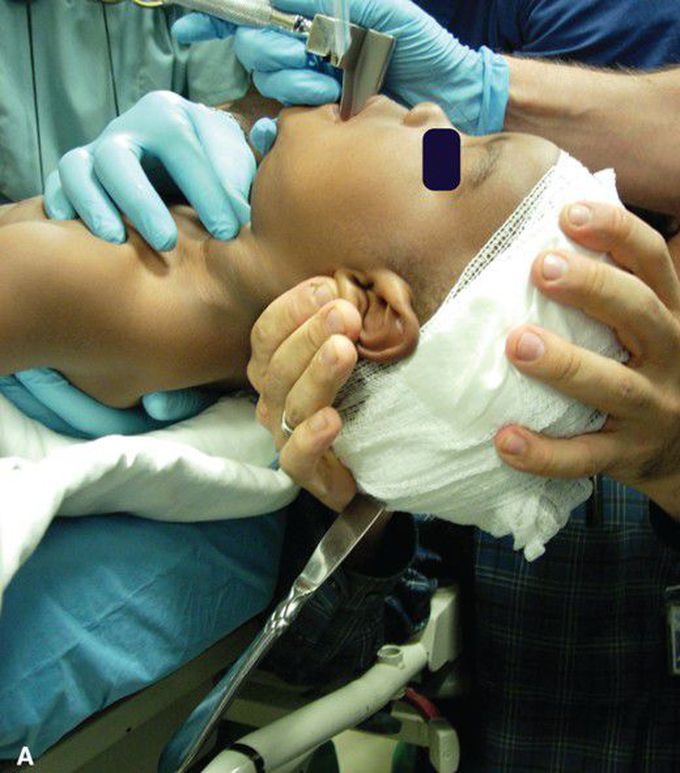
Clinical Summary Pediatric head trauma occurs commonly with most being minor; however, seemingly low-risk presentations may have intracranial injuries, and thus it is important to maintain a high index of suspicion. The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) quantifies neurologic findings and allows uniformity in description and communication among team members involved in taking care of the patient. A GCS score of 14 to 15 is categorized as mild head injury; a GCS score of 9 to 13 as moderate head injury and GCS score less than 9 as severe head injury. (A) This infant was stabbed in the head with a butter knife during a domestic dispute between his mother and angry father. He suffered no neurologic deficits after the knife was removed by neurosurgery in the operating room. (B) A lateral projection of the skull demonstrates the butter knife imbedded within the occipital-parietal region of the skull.

