

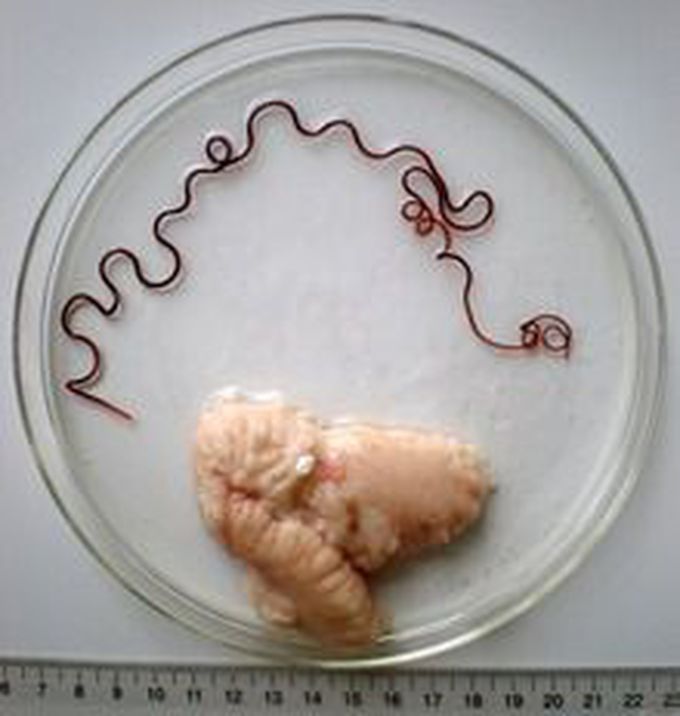
Ovary of a marine fish and its parasite
Birds have only one functional ovary (the left), while the other remains vestigial. Ovaries in females are analogous to testes in males, in that they are both gonads and endocrine glands. Ovaries of some kind are found in the female reproductive system of many animals that employ sexual reproduction, including invertebrates. However, they develop in a very different way in most invertebrates than they do in vertebrates, and are not truly homologous.[31] Many of the features found in human ovaries are common to all vertebrates, including the presence of follicular cells, tunica albuginea, and so on. However, many species produce a far greater number of eggs during their lifetime than do humans, so that, in fish and amphibians, there may be hundreds, or even millions of fertile eggs present in the ovary at any given time. In these species, fresh eggs may be developing from the germinal epithelium throughout life. Corpora lutea are found only in mammals, and in some elasmobranch fish; in other species, the remnants of the follicle are quickly resorbed by the ovary. In birds, reptiles, and monotremes, the egg is relatively large, filling the follicle, and distorting the shape of the ovary at maturity.[31] Amphibians and reptiles have no ovarian medulla; the central part of the ovary is a hollow, lymph-filled space.[32] The ovary of teleosts is also often hollow, but in this case, the eggs are shed into the cavity, which opens into the oviduct.[31] Certain nematodes of the genus Philometra are parasitic in the ovary of marine fishes and can be spectacular, with females as long as 40 cm, coiled in the ovary of a fish half this length.[33] Although most normal female vertebrates have two ovaries, this is not the case in all species. In most birds and in platypuses, the right ovary never matures, so that only the left is functional. (Exceptions include the kiwi and some, but not all raptors, in which both ovaries persist.[34][35]) In some elasmobranchs, only the right ovary develops fully. In the primitive jawless fish, and some teleosts, there is only one ovary, formed by the fusion of the paired organs in the embryo.[31]
https://www.facebook.com/PrimalTRTOfficial/Women’s Reproductive Health & Daily WellnessFlexiLeafhttps://www.facebook.com/HumeHealthBodyPodOfficial/Pulsar Vexline Review 2026 - Legit Or Scam Trading Platform? Fact CheckGelatine Sculpt | Official WebsiteBurnSlim Official | Support Your Weight Management Journey

