

Respiration & ABGs
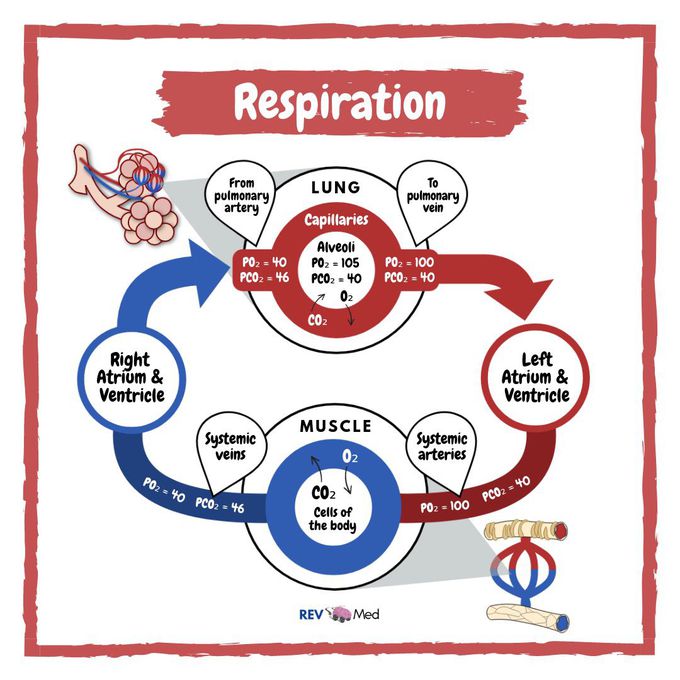
Know your ABG’s! Arterial blood gas (ABG) interpretation, something many healthcare students find difficult to understand! The Basics: You see the primary function of the respiratory system is to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide. So oxygenated blood travels from the lungs through the pulmonary veins and into the left side of the heart, which pumps the blood to the rest of the body. Oxygen-deficient, carbon dioxide-rich blood returns to the right side of the heart through two large veins, the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava. Then the blood is pumped through the pulmonary artery to the lungs, where it picks up oxygen and releases carbon dioxide. The real value of an ABG comes from its ability to provide a near immediate reflection of the physiology of your patient, allowing you to recognize and treat pathology more rapidly. Normal arterial ranges: *pH: 7.35 – 7.45 *PCO2: 4.7-6.0 kPa, 35-45 torr *PO2: 11-13 kPa, >79 torr *HCO3-: 22-26 mEq/L Base excess: -2 to +2 mmol/L The blood gas test can determine how well your patients lungs are able to move oxygen into the blood and remove carbon dioxide from the blood. Imbalances in the oxygen, carbon dioxide, and pH levels of the blood will make you say “ah HA!” and better understand your patients condition! We’ll get more into ABGs, for now head over to our YouTube channel! Subscribe (link in bio) Instagram @rev.med
https://www.facebook.com/PrimalTRTOfficial/Severe upper airway obstructionWomen’s Reproductive Health & Daily WellnessFlexiLeafhttps://www.facebook.com/HumeHealthBodyPodOfficial/Gelatine Sculpt | Official WebsiteBurnSlim Official | Support Your Weight Management Journey

