

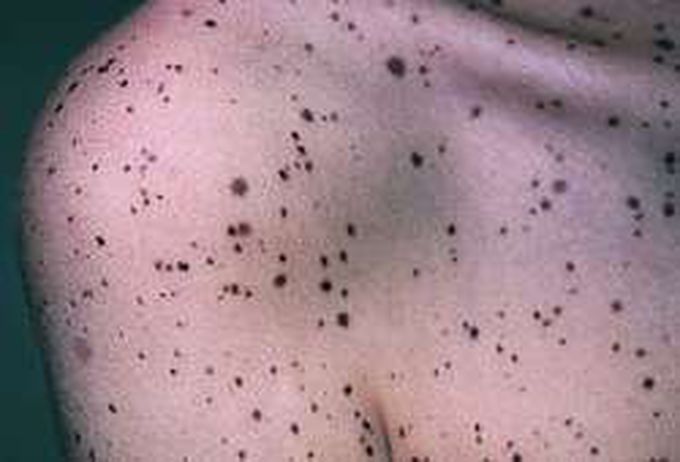
Leopard syndrome
LEOPARD syndrome is a rare genetic disorder characterized by abnormalities of the skin, the structure and function of the heart, the inner ear, the head and facial (craniofacial) area, and/or the genitals. LEOPARD syndrome: A genetic syndrome transmitted in an autosomal dominant manner that is named for its characteristic features: L -- lentigines (dark freckles) on the head and neck E -- electrocardiogram (EKG) abnormalities O -- ocular hyperteleorism (wide-spacing of the eyes) P -- pulmonary stenosis A -- abnormal genitalia R -- retardation of growth D -- deafness (sensorineural type) The LEOPARD syndrome is caused by mutations in the gene for protein-tyrosine phosphatase, nonreceptor-type, 11 (PTPN11). The LEOPARD syndrome is therefore allelic with Noonan syndrome which is also the result of mutations in PTPN11. LEOPARD syndrome is the most common name for the disorder. It is also known as multiple lentigines syndrome, Gorlin syndrome II, cardio-cutaneous syndrome, lentiginosis profusa syndrome, progressive cardiomyopathic lentiginosis.


