

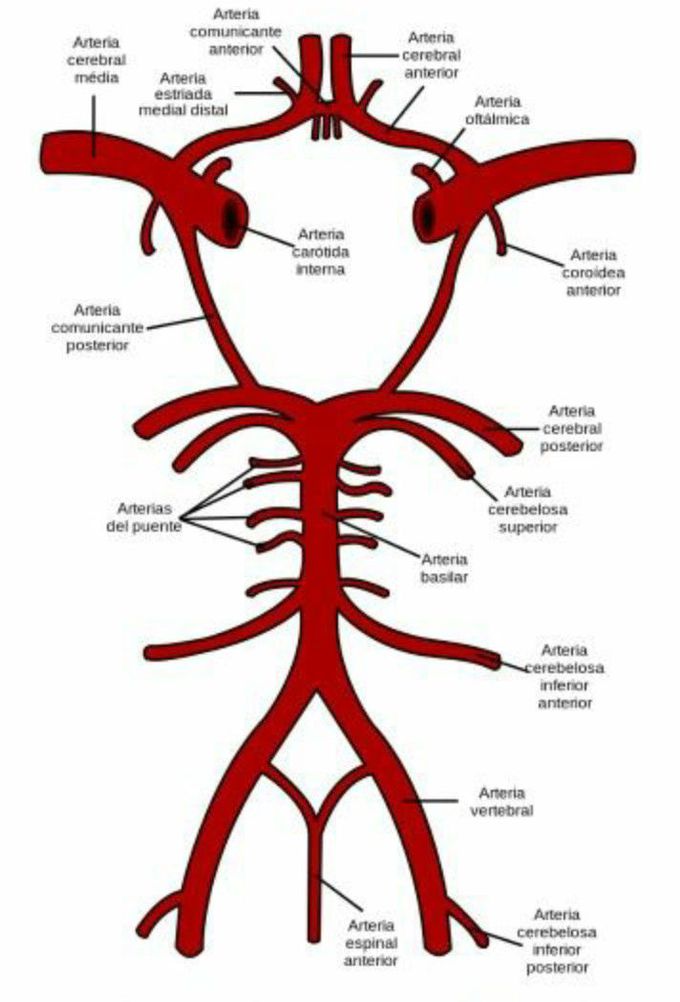
Circulation cerebral
The rate of the cerebral blood flow in the adult is typically 750 milliliters per minute, representing 15% of the cardiac output. The arteries deliver oxygenated blood, glucose and other nutrients to the brain, and the veins carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart, removing carbon dioxide, lactic acid, and other metabolic products. Since the brain is very vulnerable to compromises in its blood supply, the cerebral circulatory system has many safeguards including autoregulation of the blood vesselsand the failure of these safeguards can result in a stroke. The amount of blood that the cerebral circulation carries is known as cerebral blood flow. The presence of gravitational fields or accelerations also determine variations in the movement and distribution of blood in the brain, such as when suspended upside-down

