

Zunaira salehabout 1 year ago
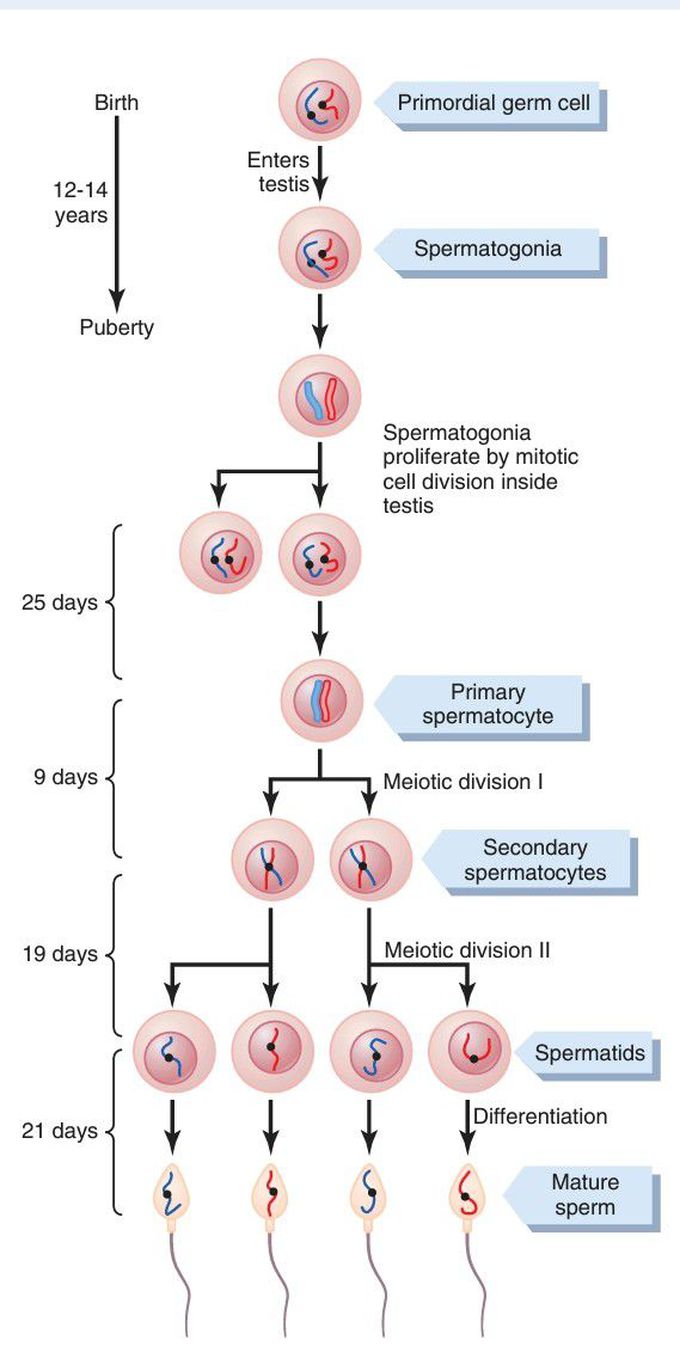
Cell divisions during spermatogenesis.
During embryonic development, the primordial germ cells migrate to the testis, where they become spermatogonia. At puberty (usually 12 to 14 years after birth), the spermatogonia proliferate rapidly by mitosis. Some begin meiosis to become primary spermatocytes and continue through meiotic division I to become secondary spermatocytes. After completion of meiotic division II, the secondary spermatocytes produce spermatids, which differentiate to form spermatozoa.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!

