

Zunaira saleh12 months ago
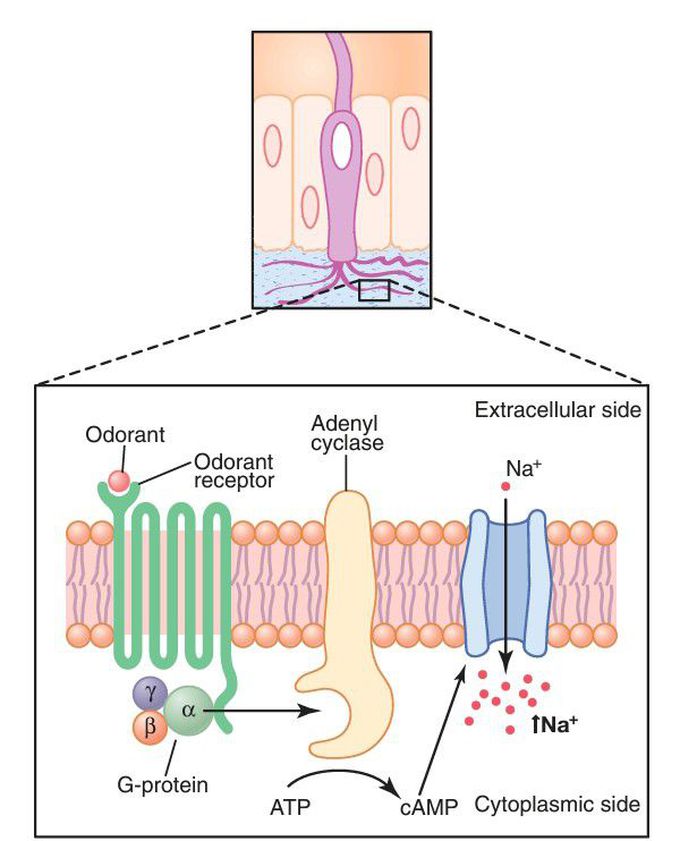
Summary of olfactory signal transduction
. Binding of the odorant to a G-protein–coupled receptor causes activation of adenylate cyclase, which converts ATP to cAMP. The cAMP activates a gated sodium channel that increases sodium influx and depolarizes the cell, exciting the olfactory neuron and transmitting action potentials to the central nervous system.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!

