

Zunaira salehabout 1 year ago
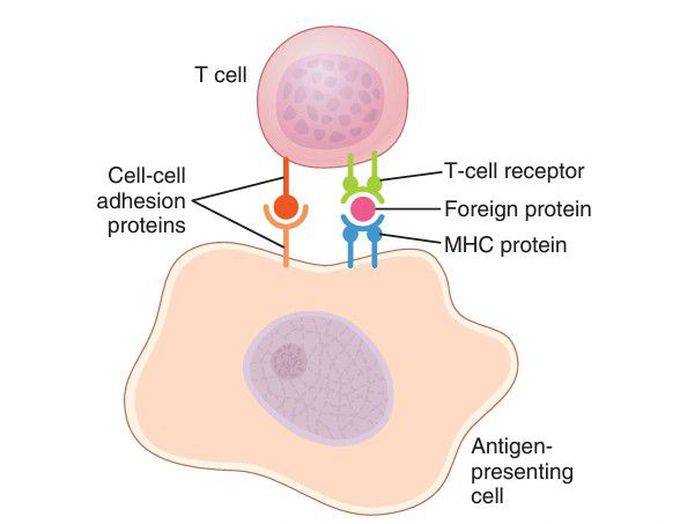
Activation of T cell
Activation of T cells requires interaction of T-cell receptors with an antigen (foreign protein) that is transported to the surface of the antigen-presenting cell by a major histocompatibility complex (MHC) protein. Cell-to-cell adhesion proteins enable the T cell to bind to the antigen-presenting cell long enough to become activated.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!

