

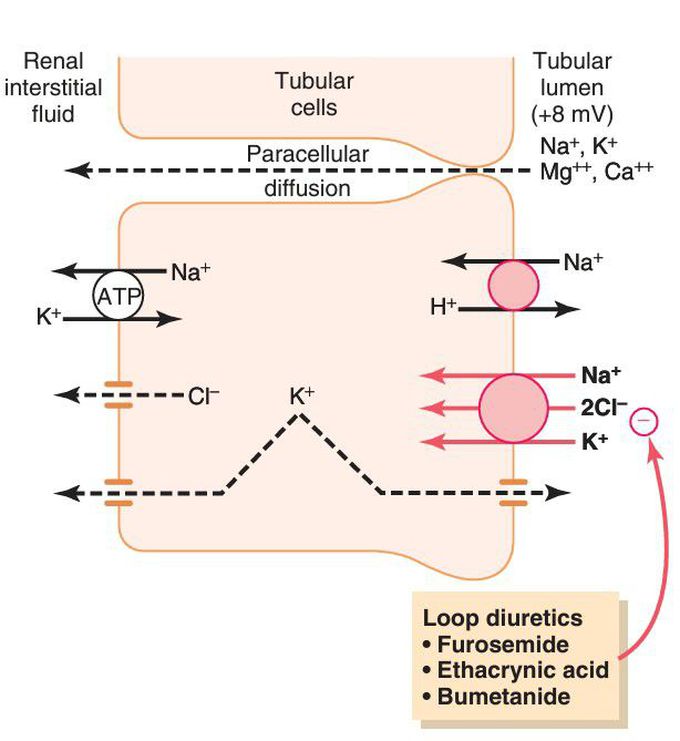
Thick ascending loop 9f henle
Mechanisms of sodium, chloride, and potassium transport in the thick ascending loop of Henle. The sodium-potassium ATPase pump in the basolateral cell membrane maintains a low intracellular sodium concentration and a negative electrical potential in the cell. The 1-sodium, 2-chloride, 1-potassium co-transporter in the luminal membrane transports these three ions from the tubular lumen into the cells, using the potential energy released by diffusion of sodium down an electrochemical gradient into the cells. Sodium is also transported into the tubular cell by sodium-hydrogen counter-transport. The positive charge (+8 mV) of the tubular lumen relative to the interstitial fluid forces cations such as Mg++ and Ca++ to diffuse from the lumen to the interstitial fluid via the paracellular pathway.

