

Zunaira salehabout 1 year ago
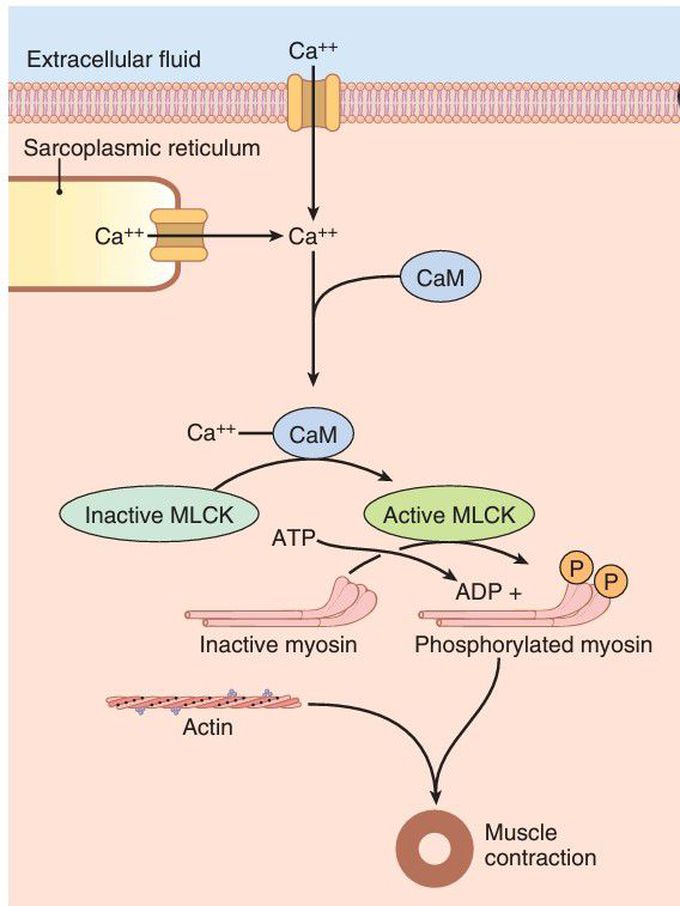
Calcium calmodulin complex
Intracellular calcium ion (Ca++) concentration increases when Ca++ enters the cell through calcium channels in the cell membrane or is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The Ca++ binds to calmodulin (CaM) to form a Ca++-CaM complex, which then activates myosin light chain kinase (MLCK). The active MLCK phosphorylates the myosin light chain leading to attachment of the myosin head with the actin filament and contraction of the smooth muscle. ADP, adenosine diphosphate; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; P, phosphate.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!
Related posts

