

Treatment of esophageal varices
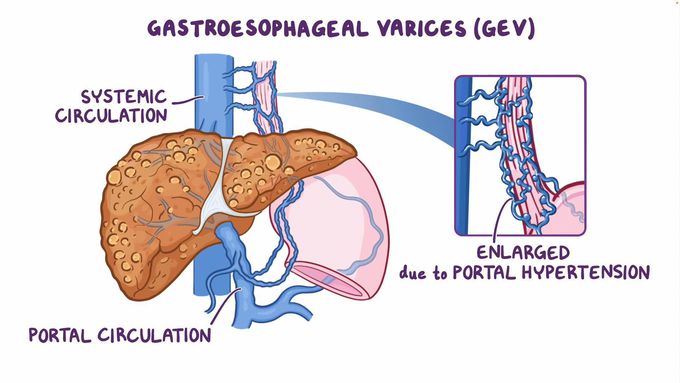
The main goal of treatment for esophageal varices is to prevent ruptures and bleeding. Initially, this often involves steps to control portal hypertension. The doctor may prescribe beta-blockers to reduce blood pressure. These drugs work by blocking the effects of a hormone called epinephrine, making the heart beat slower and with less force. A person with esophageal varices may also require one of the following surgical procedures. Endoscopic sclerotherapy involves using an endoscope to perform minor medical tasks, such as injecting a medication into the swollen veins to make them shrink. Endoscopic variceal banding involves using the same tool to place a rubber band around a varice to prevent the vessel from bleeding. Additional treatments may be necessary for varices that bleed recurrently. A doctor may recommend a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt, or TIPS, procedure. This involves using an X-ray to guide the placement of a small tube to connect the portal vein with the hepatic vein. This creates a new channel for blood, reducing pressure in the portal vein. Another treatment option is a distal splenorenal shunt procedure. This connects the main vein of the spleen to the vein of the left kidney.

