

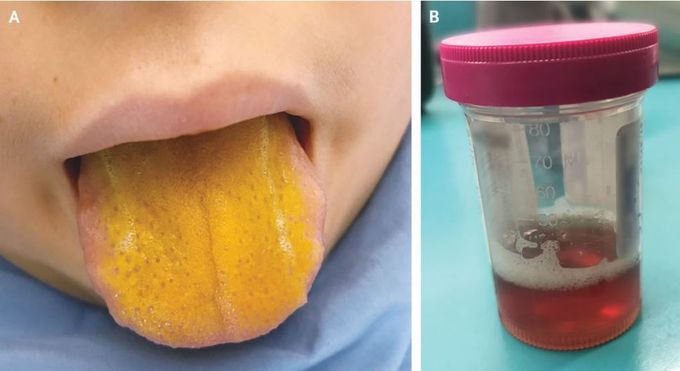
Yellow tongue
A yellow tongue isn't usually cause for alarm — a number of ordinary things can turn the tongue the color of mustard, from a dry mouth to bad oral hygiene. But for a 12-year-old boy in Canada, a yellow tongue was a sign of a serious and rare disorder. The boy went to the hospital after he experienced a sore throat, dark urine, abdominal pain and pale skin for several days, according to the report, published July 24 in The New England Journal of Medicine. He also had a bright yellow tongue. Doctors determined that the boy had jaundice, a condition that usually causes a yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes as well as dark urine, and in rare cases can cause a yellow tongue, Live Science previously reported. Jaundice happens when a yellow chemical called bilirubin builds up in the body. Bilirubin is formed during the normal breakdown of red blood cells. But what was causing the boy's jaundice? After running a number of tests, doctors determined that the boy had cold agglutinin disease, a rare autoimmune disorder in which a person's immune system attacks and destroys its own red blood cells. This autoimmune attack is triggered by exposure to cold temperatures, and so symptoms can be worse during winter months. The condition results in anemia and may also cause jaundice because the fast breakdown of red blood cells leads to a buildup of bilirubin. In some cases, cold agglutinin disease may be caused by certain infections, including infections with Epstein-Barr virus. The boy was found to have an infection with Epstein–Barr virus, and his doctors suspect the infection triggered the boy's cold agglutinin disease. The boy needed a blood transfusion and received treatment with oral steroids to reduce immune system activity. After the boy left the hospital, he "recovered well," and his tongue color gradually returned to normal as levels of bilirubin in his body fell, the authors said.

