
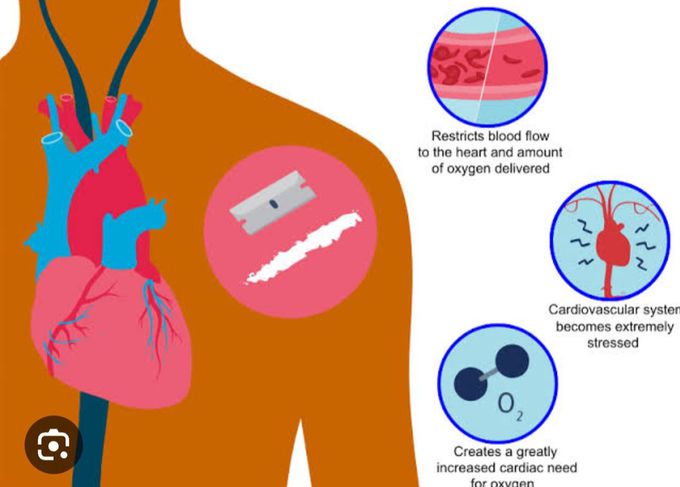
Cocaine related Angina
Cocaine has sympathomimetic effects that induce tachycardia and hypertension, resulting in an increased myocardial-oxygen demand. When this demand exceeds the supply, myocardial ischemia occurs. But unlike the conventional angina, beta-blockers are contraindicated in cocaine-angina, as they increase the effect of alpha-receptors and worsen hypertension and chest pain. Chest pain in cocaine intoxication is treated with benzodiazepines.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!
Related posts
Supraventricular TachycardiaSupraventricular tachycardia- DiagnosisPatent Ductus Arteriosus- SymptomsAtrial Septal Defect- DiagnosisSymptoms of dengue
https://www.facebook.com/PrimalTRTOfficial/https://www.facebook.com/AspenDoseCBDGummiesPage/https://www.facebook.com/PrimalTRTOfficial/Gelatide Drops | Official Metabolic Wellness Website
https://www.facebook.com/PrimalTRTOfficial/https://www.facebook.com/AspenDoseCBDGummiesPage/https://www.facebook.com/PrimalTRTOfficial/Gelatide Drops | Official Metabolic Wellness Website

