
Just Knowledge.....
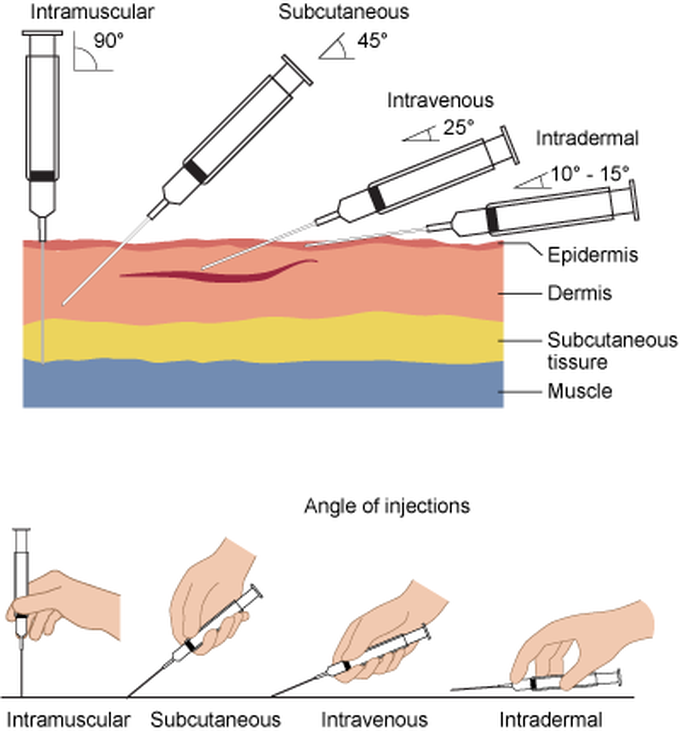
Injection (often referred to as a "shot" in US English, or a "jab" in UK English) is the act of putting a liquid, especially a drug, into a person's body using a needle (usually a hypodermic needle) and a syringe.[1] Injection is a technique for delivering drugs by parenteral administration, that is, administration via a route other than through the digestive tract. Parenteral injection includes subcutaneous, intramuscular, intravenous, intraperitoneal, intracardiac, intraarticular and intracavernous injection. Injection is generally administered as a bolus, but can possibly be used for continuous drug administration as well.[2] Even when administered as a bolus, the medication may be long-acting, and can then be called depot injection. Administration by an indwelling catheter is generally preferred instead of injection in case of more long-term or recurrent drug administration.

