

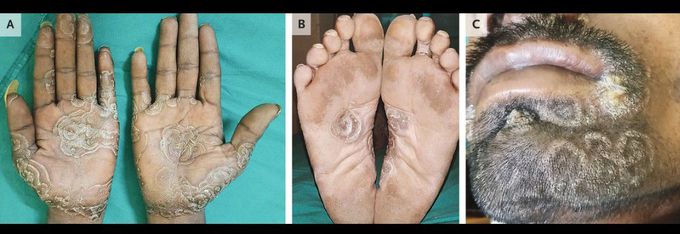
Circinate Syphilitic Lesions
A 30-year-old man presented to the sexual health clinic with a rash on his face, hands, and feet that had appeared 1 month earlier. He had a history of human immunodeficiency virus infection; his most recent CD4+ T-cell count was 374 per cubic millimeter. He reported having had unprotected sexual intercourse 2 months earlier. A physical examination showed circinate, concentric lesions on the palms (Panel A) and soles (Panel B). Multiple circinate lesions were also visible on the face, with areas of erosion at the oral commissures (Panel C). Condyloma latum was present in the perianal area, and patchy alopecia was visible on the scalp. A Venereal Disease Research Laboratory (VDRL) test was positive at a titer of 1:32, which confirmed a diagnosis of syphilis. Tests for other sexually transmitted infections were negative. The patient was treated with intramuscular benzathine penicillin. At a follow-up visit 1 month after the initiation of treatment, all the lesions had completely resolved. A repeat VDRL test showed a reduced titer of 1:8.

