

Criteria and classification of juvenile idiopathic arthritis
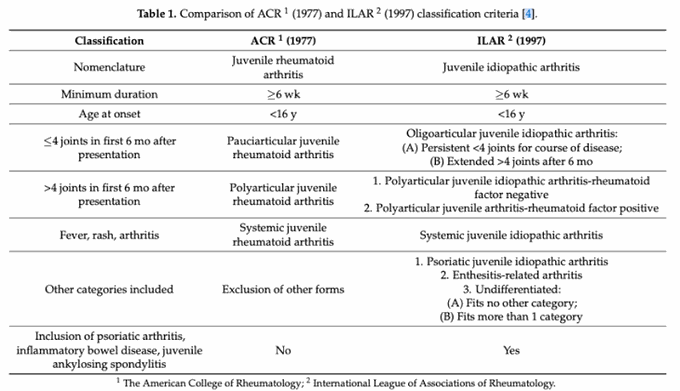
Criteria and classification Three groups have developed sets of criteria to classify children with arthritis: the American College of Rheumatology (ACR), the European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR), and the International League of Associations for Rheumatology (ILAR). The ACR criteria define juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (JRA) by age limit (< 16 y) and the duration of disease (>6 weeks). (See Table.) The organization recognizes the following 3 subtypes: Polyarticular Pauciarticular Systemic Other forms of childhood arthritis, such as juvenile ankylosing spondylitis and psoriatic arthritis, are classified under spondyloarthropathies. The ILAR classification of JIA includes the following categories: Systemic-onset JIA Persistent or extended oligoarthritis Rheumatoid factor (RF)–positive polyarthritis RF-negative polyarthritis Psoriatic JIA Enthesitis-related arthritis Undifferentiated - The disease does not meet criteria for any of the other subgroups, or it meets more than 1 criterion (and therefore could be classified in a number of subgroups). The EULAR proposed the term juvenile chronic arthritis (JCA) for the heterogeneous group of disorders that manifest as juvenile arthritis. The diagnosis requires that the arthritis begins before age 16 years and lasts for at least 3 months. The EULAR criteria for JCA recognize the following subtypes, based on characteristics at onset: Pauciarticular (1-4 joints) Polyarticular (≥5 joints) Presence of RF (2 positive tests at least 3 months apart) Systemic onset with characteristic features Positivity for rheumatoid factor Juvenile ankylosing spondylitis Juvenile psoriatic arthritis

