

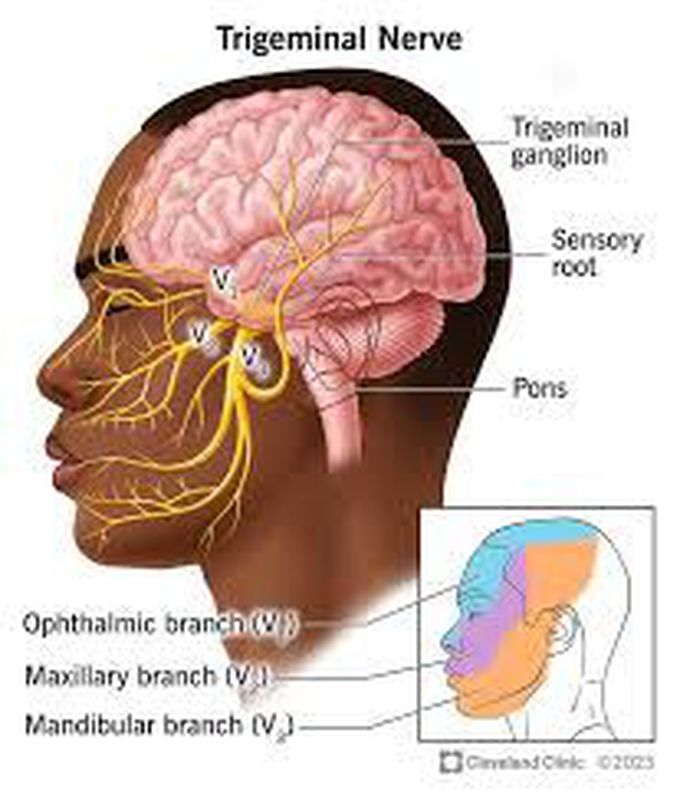
Cause of trigeminal neuralgia
tests also can help your doctor determine if your symptoms are caused by a compressed nerve or another condition. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Your doctor may order an MRI scan of your head to determine if multiple sclerosis or a tumor is causing trigeminal neuralgia. In some cases, your doctor may inject a dye into a blood vessel to view the arteries and veins and highlight blood flow. Your facial pain may be caused by many different conditions, so an accurate diagnosis is important. Your doctor may order additional tests to rule out other conditions. Care at Mayo Clinic Our caring team of Mayo Clinic experts can help you with your trigeminal neuralgia-related health concerns Start Here More Information Trigeminal neuralgia care at Mayo Clinic MRI Treatment Trigeminal neuralgia treatment usually starts with medications, and some people don't need any additional treatment. However, over time, some people with the condition may stop responding to medications, or they may experience unpleasant side effects. For those people, injections or surgery provide other trigeminal neuralgia treatment options. If your condition is due to another cause, such as multiple sclerosis, your doctor will treat the underlying condition. Medications To treat trigeminal neuralgia, your doctor usually will prescribe medications to lessen or block the pain signals sent to your brain. Anticonvulsants. Doctors usually prescribe carbamazepine (Tegretol, Carbatrol, others) for trigeminal neuralgia, and it's been shown to be effective in treating the condition. Other anticonvulsant drugs that may be used to treat trigeminal neuralgia include oxcarbazepine (Trileptal, Oxtellar XR), lamotrigine (Lamictal), valproate and phenytoin (Dilantin, Phenytek, Cerebyx). Other drugs, including clonazepam (Klonopin), topiramate (Qsymia, Topamax, others), pregabalin (Lyrica) and gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant), also may be used. If the anticonvulsant you're using begins to lose effectiveness, your doctor may increase the dose or switch to another type. Side effects of anticonvulsants may include dizziness, confusion, drowsiness and nausea. Also, carbamazepine can trigger a serious drug reaction in some people, mainly those of Asian descent, so genetic testing may be recommended before you start carbamazepine. Antispasmodic agents. Muscle-relaxing agents such as baclofen (Gablofen, Lioresal, Ozobax) may be used alone or in combination with carbamazepine. Side effects may include confusion, nausea and drowsiness. Botox injections. Small studies have shown that onabotulinumtoxinA (Botox) injections may reduce pain from trigeminal neuralgia in people who are no longer

