

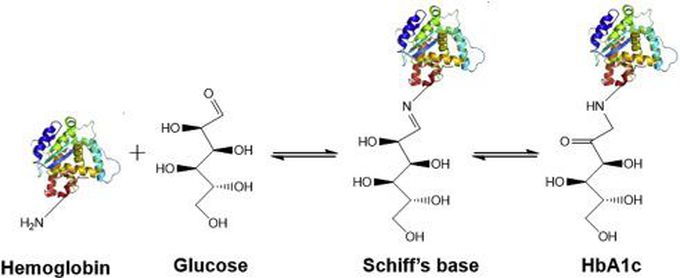
Glycated hemoglobin
Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) is a laboratory test used to assess long-term blood glucose control in patients with diabetes mellitus. HbA1c is a form of hemoglobin that is formed when red blood cells bind to glucose and remains in the blood for a longer period of time than nonglycated hemoglobin, thus providing a measure of the average blood glucose level over the past 8-12 weeks. The bond that is formed between hemoglobin and glucose leads to the formation of a schiff base, which causes molecular rearrangements that produce AGEs, or advanced glycation products that can trigger inflammatory processes and lead in the long run to atherosclerotic diseases. HbA1c is expressed as a percentage, and the goal of treatment for diabetes mellitus is to keep HbA1c below 7 percent, which indicates an average blood glucose level over the past 8 to 12 weeks of less than 154 mg/dL.However, there are some situations in which the HbA1c test may be unreliable, such as in the case of people with sickle cell anemia or other forms of abnormal hemoglobin, who may have falsely low or falsely high results. In addition, patients with chronic kidney disease or type 1 diabetes may have reduced hemoglobin half-life and thus falsely low results.

