

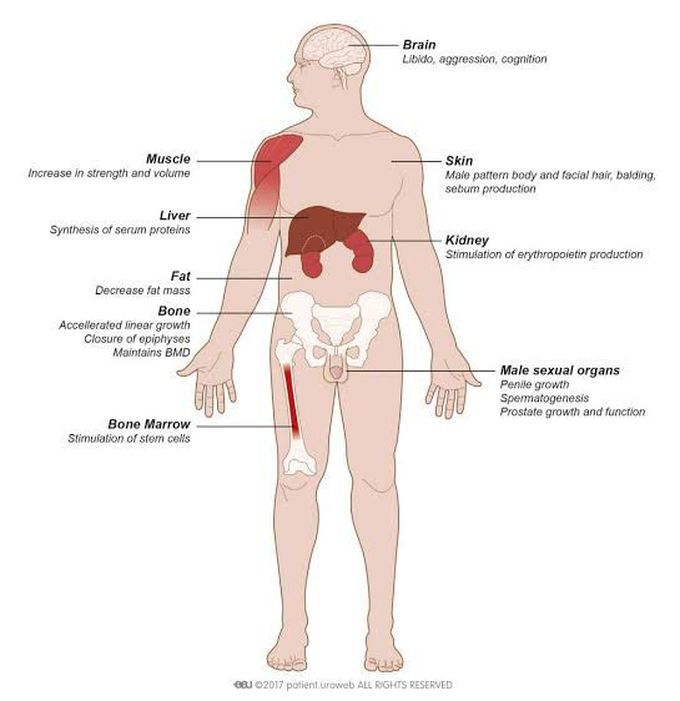
symptoms of male hypogonadism
Hypogonadism can begin during fetal development, before puberty or during adulthood. Signs and symptoms depend on when the condition develops. Fetal development If the body doesn't produce enough testosterone during fetal development, the result may be impaired growth of the external sex organs. Depending on when hypogonadism develops and how much testosterone is present, a child who is genetically male may be born with: Female genitals Genitals that are neither clearly male nor clearly female (ambiguous genitals) Underdeveloped male genitals Puberty Male hypogonadism can delay puberty or cause incomplete or lack of normal development. It can hamper: Development of muscle mass Voice deepening Growth of body and facial hair Growth of the penis and testicles And it can cause: Excessive growth of the arms and legs in relation to the trunk of the body Development of breast tissue (gynecomastia) Adulthood In adult males, hypogonadism can alter certain masculine physical characteristics and impair normal reproductive function. Early signs and symptoms might include: Decreased sex drive Decreased energy Depression Over time, men with hypogonadism can develop: Erectile dysfunction Infertility Decrease in hair growth on the face and body Decrease in muscle mass Development of breast tissue (gynecomastia) Loss of bone mass (osteoporosis)

