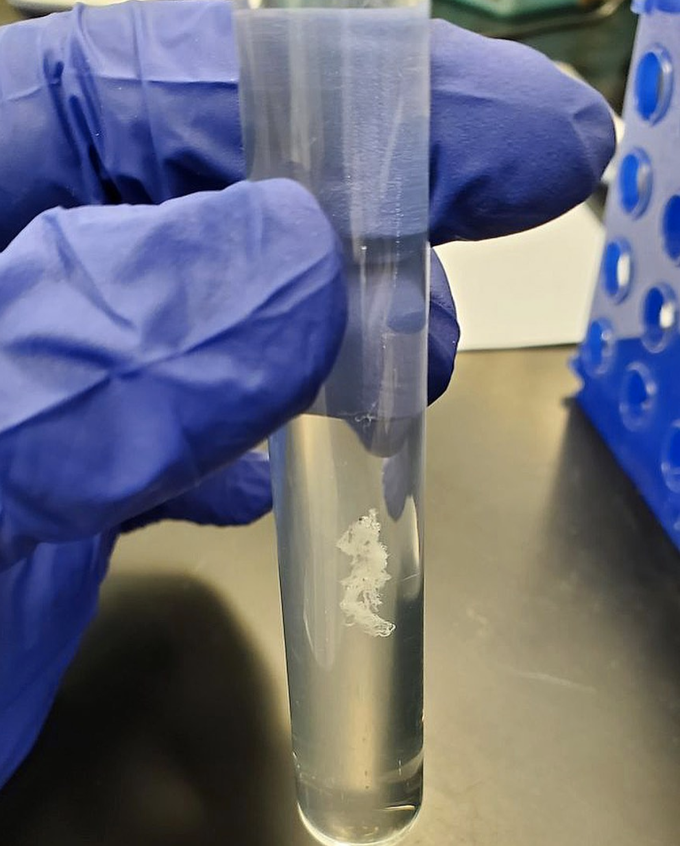


Purified DNA strands in a test tube!!
DNA, which stands for Deoxyribonucleic acid, is made up molecules known as nucleic acids. These were first identified by Swiss physician and biologist Johannes Friedrich Miescher in 1869, who called them “nuclein” because they were found in the nucleus of the cell. Every type of life form known contains nucleic acids, in the form of DNA or RNA (ribonucleic acid). The genetic information of an organism is stored in the form of nucleic acids. Nucleic acids, DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid), are long linear polymers composed of nucleotide building blocks. Each nucleotide is comprised of a sugar, a phosphate residue, and a nitrogenous bases (a purine or pyrimidine). DNA is longer than RNA and contains the entire genetic information of an organism encoded in the sequences of the bases. In contrast, RNA only contains a portion of the information and can have completely different functions in the cell.

