

Causes of melanoma
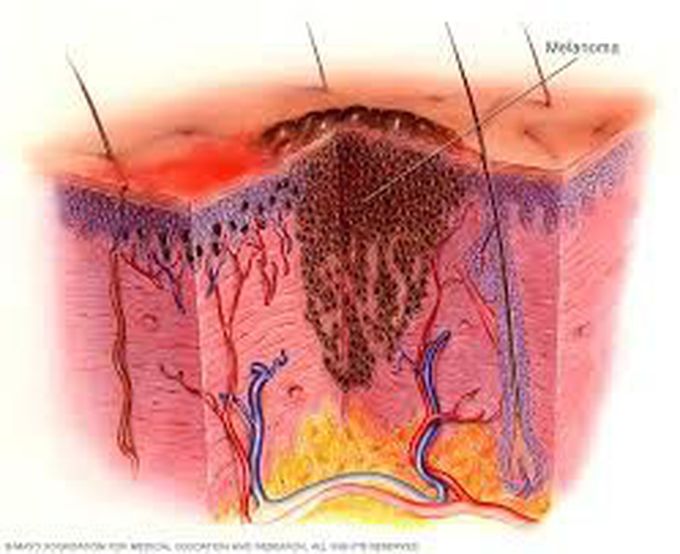
Causes Where skin cancer develops Where skin cancer developsOpen pop-up dialog box Melanoma occurs when something goes wrong in the melanin-producing cells (melanocytes) that give color to your skin. Normally, skin cells develop in a controlled and orderly way — healthy new cells push older cells toward your skin's surface, where they die and eventually fall off. But when some cells develop DNA damage, new cells may begin to grow out of control and can eventually form a mass of cancerous cells. Just what damages DNA in skin cells and how this leads to melanoma isn't clear. It's likely that a combination of factors, including environmental and genetic factors, causes melanoma. Still, doctors believe exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun and from tanning lamps and beds is the leading cause of melanoma. UV light doesn't cause all melanomas, especially those that occur in places on your body that don't receive exposure to sunlight. This indicates that other factors may contribute to your risk of melanoma. Risk factors Factors that may increase your risk of melanoma include: Fair skin. Having less pigment (melanin) in your skin means you have less protection from damaging UV radiation. If you have blond or red hair, light-colored eyes, and freckle or sunburn easily, you're more likely to develop melanoma than is someone with a darker complexion. But melanoma can develop in people with darker complexions, including Hispanic people and black people. A history of sunburn. One or more severe, blistering sunburns can increase your risk of melanoma. Excessive ultraviolet (UV) light exposure. Exposure to UV radiation, which comes from the sun and from tanning lights and beds, can increase the risk of skin cancer, including melanoma. Living closer to the equator or at a higher elevation. People living closer to the earth's equator, where the sun's rays are more direct, experience higher amounts of UV radiation than do those living farther north or south. In addition, if you live at a high elevation, you're exposed to more UV radiation.

